CompTIA Security+ SY0-601 - Objectives Notes
Queste sono le mie personali note prese durante lo studio per la CompTIA Security+. Sono quasi interamente definizioni e domande di pratica per testare la comprensione di alcuni termini e fare in modo ricordare anche i più complessi.
La maggior parte degli appunti sono stati presi guardando i video della CompTIA Security+ SY0-601 Training Course del Professor Messer. Lo ringrazio infinitamente per avermi aiutato a prendere questa certificazione. Spero che questi miei appunti ti siano utili.
Navigazione:
- Per capitolo (codici 1.0, 1.1)
- Per Titolo:
- 1.0 Threats, Attacks and Vulnerabilities
- 2.0 Architecture and Design
- 3.0 Implementation
- 4.0 Operations and Incident Response
- 5.0 Governance, Risk and Compliance
Qui una lista completa degli objectives.
1.0 - Threats, Attacks and Vulnerabilities
1.1 Terminology
Phishing
Social engineering combined with Spoofing.
- Delivered by email.
- Something not quite right.
Look the domain name, it could fool you.
Impersonation
Starts with a lie that set the scenario. There’s an actor and a story.
Attackers pretend to be someone they aren’t
It’s done to:
- Extracting informations
- identity fraud
To protect yourself:
![Schermata_2021-06-29_alle_19.36.15.png]()
Dumpster Diving
a way to gather information from someone in a silent way.
in a word, it is osint.
to protect you have to secure all you garbage documents.
Shoulder surfing
someone looking your screen behind you
Hoaxes (Uomini e Donne)
a situation that’s not real but seems like it could be.
Watering Hole Attacks
Third party where they want you to come in to infect you.
They search for vulnerabilities in the site they want to use as the Watering Hole.
To prevent it use layered defense
How to Avoid Spam?
Teach your Company and automatize the process of email filtering
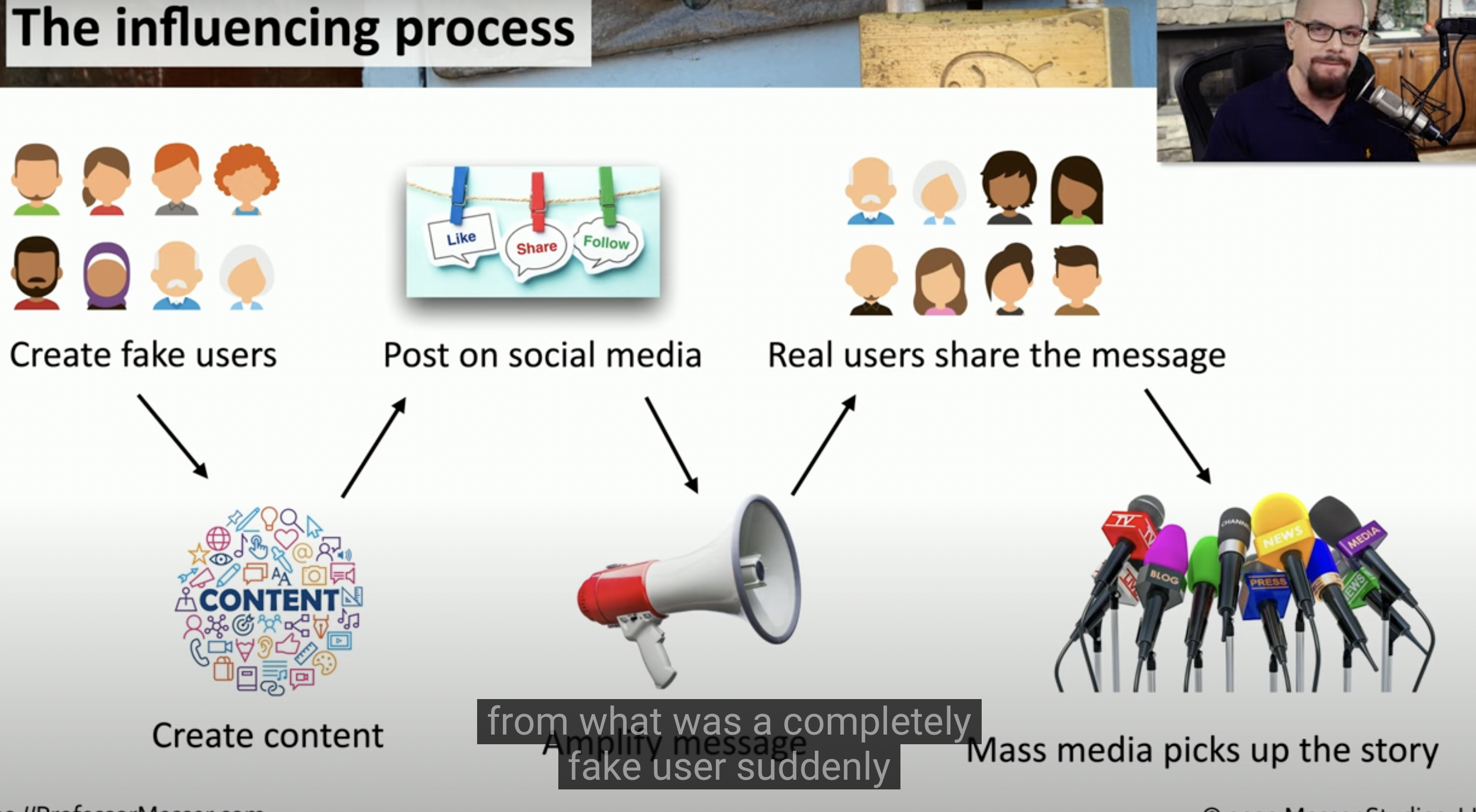
Influencing Process consists in…
Social Engeneering
![Schermata 2021-08-26 alle 16.48.25.png]()
Tailgating
Someone that gains access with your credentials, for example someone you keep the door open for
1.2
Viruses and Worms
Name at least 5 types of malware
![Schermata 2021-08-26 alle 17.36.26.png]()
Differences between viruses and worms
Viruses requires human beings to start the process of replication
Worms don’t
Virus Types
![Schermata 2021-08-26 alle 17.45.38.png]()
Fileless Viruses
Never saves himself, it operates solely in the memory without writing the disk
Name a Famous 2017 Worm
WannaCry Ransomware
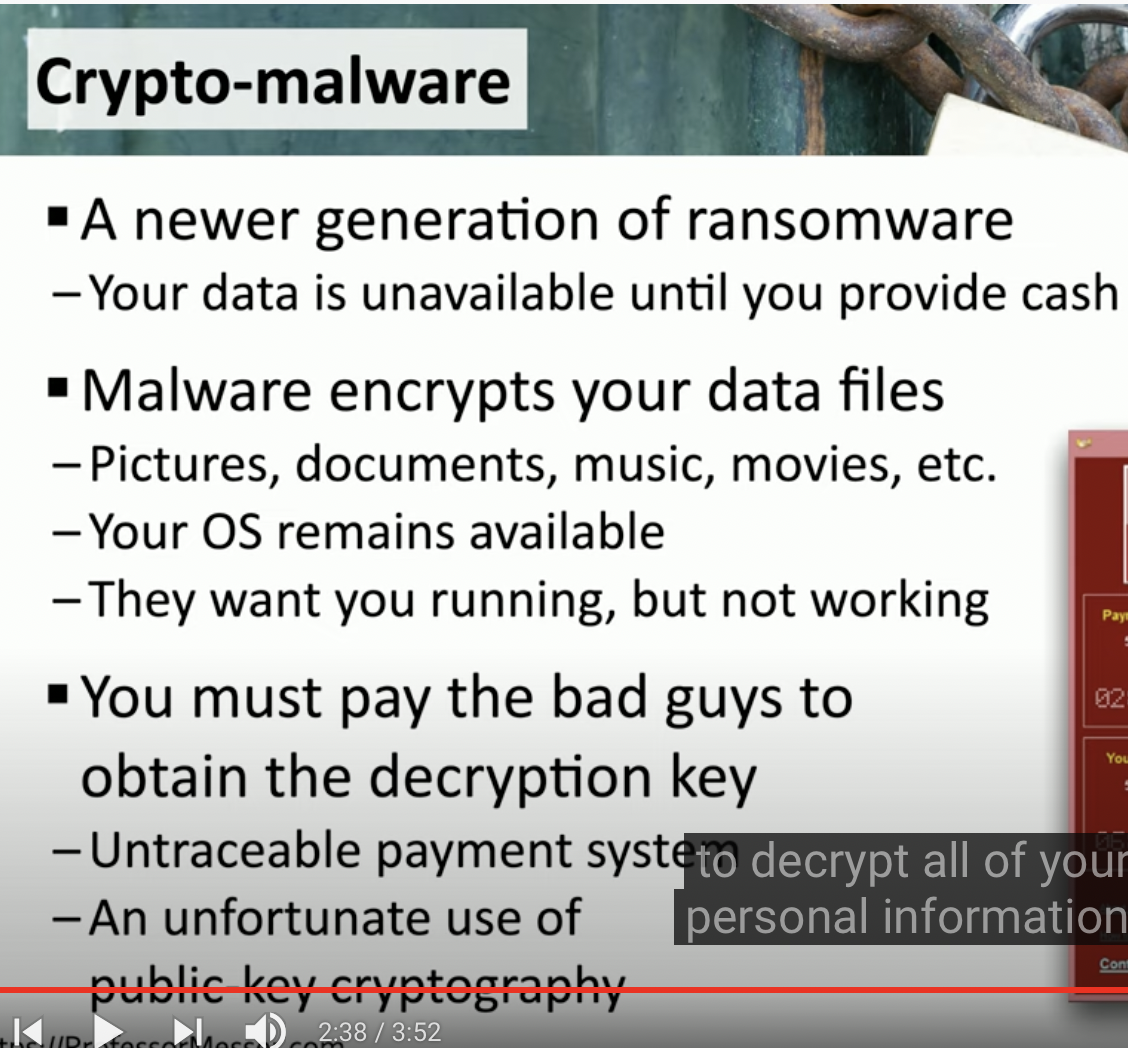
Ransomware and Crypto-malware
Features of Crypto-Malware
![Schermata 2021-08-26 alle 17.54.16.png]()
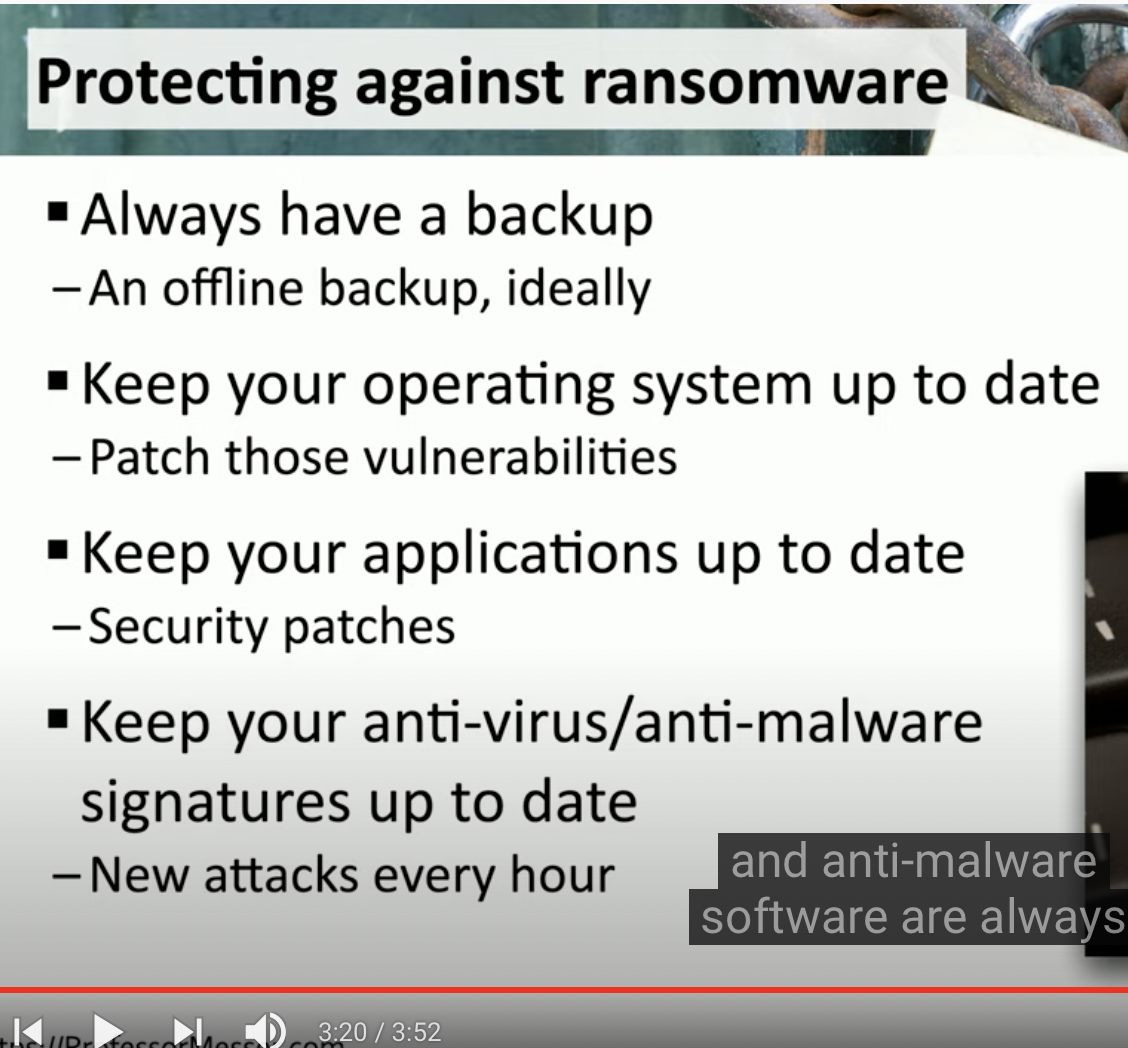
How to be protected against Ransomware
![Schermata 2021-08-26 alle 17.55.16.png]()
Trojan and RATs
Trojan
Software that pretends to be something else. You have to manually install it
What is a PUP? (potentially…)
Potentially Unwanted Program
Most common way to maintain access?
Backdoors
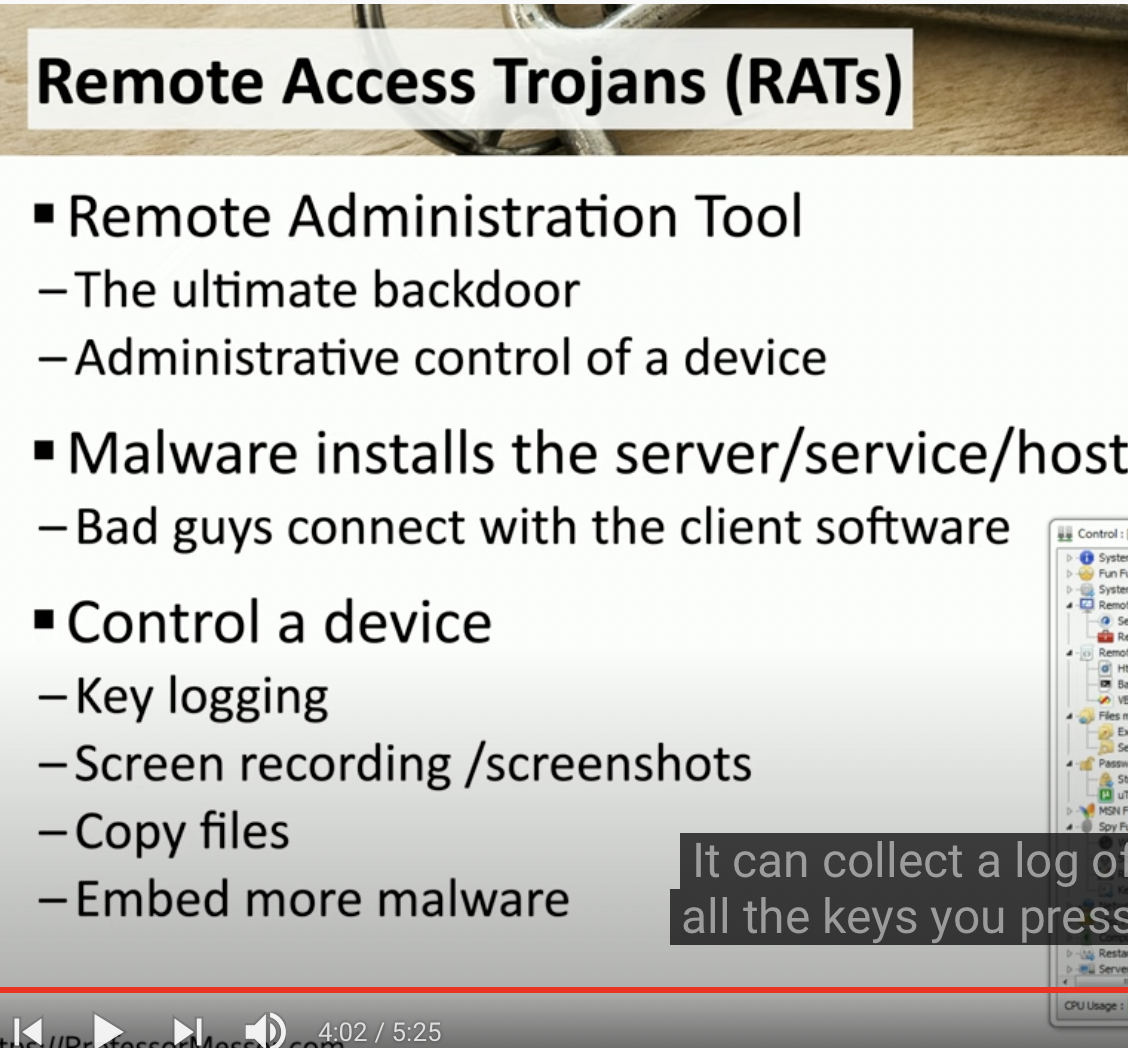
RAT stands for …
Remote Access Trojan
What can a RAT do?
![Schermata 2021-08-26 alle 18.01.46.png]()
Rootkit
What does a Rootkit do?
It modifies kernel parts and core system files. So it becomes invisible to anti-virus and a part of the OS itself.
How could an attacker combine a malware and a rootkit?
Using the rootkit to block the possibility of deleting the malware and terminates its processes
Spyware
How not to remove adware
Using adware affiliate ‘software uninstaller’. use antivirus or the prompt to remove them properly
What does a Spyware tries to do?
![Schermata 2021-08-26 alle 18.12.29.png]()
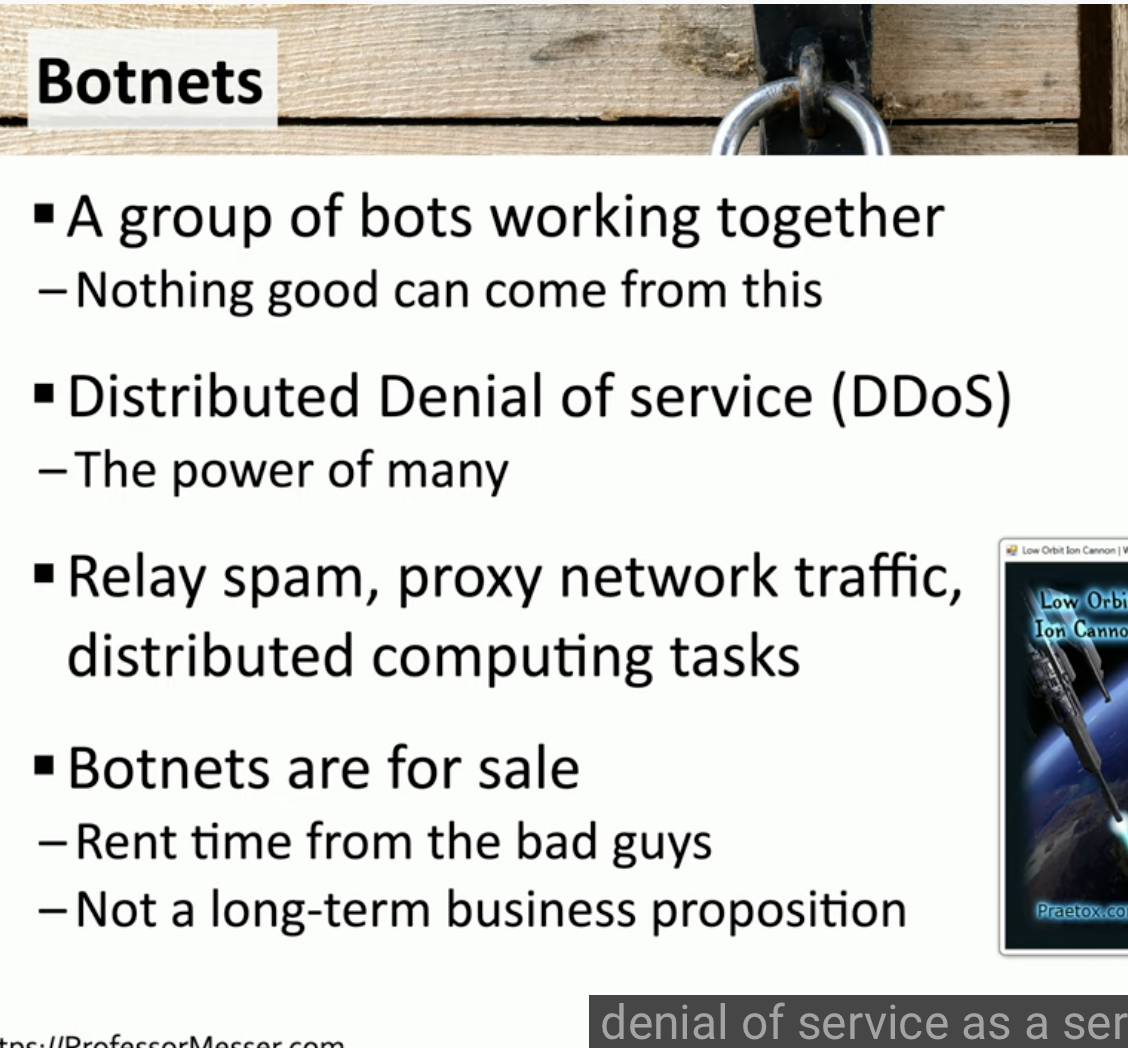
Bots and BotNets
Botnets
![Schermata 2021-08-26 alle 18.32.02.png]()
How to spot them
Monitor the network. Prevent for C&C (command and control) and block it at the firewall
How to prevent them
Prevent for C&C (command and control) and block it at the firewall
Logic Bombs
What is a Logic Bomb
A malicious piece of software that activates himself in a determined time or in other peculiar situations
How to spot a Logic Bomb
You can’t
![Schermata 2021-08-26 alle 18.40.10.png]()
Password Attacks
Spring
Makes around 3 tries for account
What’s more effective than Brute Force if you have the hash?
Rainbow Table Attacks
How to prevent Tables Attacks?
Adding Salt
Physical Attacks
Malicious USB cable
Just put something malicious on a cable
Malicious Flash drive
![Schermata 2021-08-27 alle 09.00.13.png]()
![Schermata 2021-08-27 alle 09.01.18.png]()
What does Skimming means?
![Schermata 2021-08-27 alle 09.02.30.png]()
Adversarial Artificial intelligence
Tell me one downside of Machine learning
Requires a lot of training data
![Schermata 2021-08-27 alle 09.09.21.png]()
Supply Chain Attacks
What does a supply chain is made of?
![Schermata 2021-08-27 alle 09.13.44.png]()
How does someone gain access thanks to Supply Chains?
People trust his supplies. If someone can get into you network and in the inside you ain’t got any protection (internal pentesting), your network is f**d up.
How to avoid it?
Put internal protections. Separate networks.
On-Premises vs Cloud Based Attacks
Upsides and Downsides of the on-premises Security
![Schermata 2021-08-27 alle 09.27.05.png]()
Upsides and Downsides of the Cloud Based choice
![Schermata 2021-08-27 alle 09.28.20.png]()
Cryptographic Attacks
Are hash digests supposed to be unique?
yes. do not let them collide
What is a Downgrade Attack
![Schermata 2021-08-27 alle 09.34.27.png]()
1.3
Privilege escalation
How can a normal user gain root access in a network?
Through privilege escalation, which is done by exploiting vulnerabilities.
This are the most important to patch. Do you remember how to mitigate it?
![Schermata 2021-08-27 alle 09.39.35.png]()
Cross-Site Scripting (XSS)
XSS
![Schermata 2021-08-28 alle 12.01.21.png]()
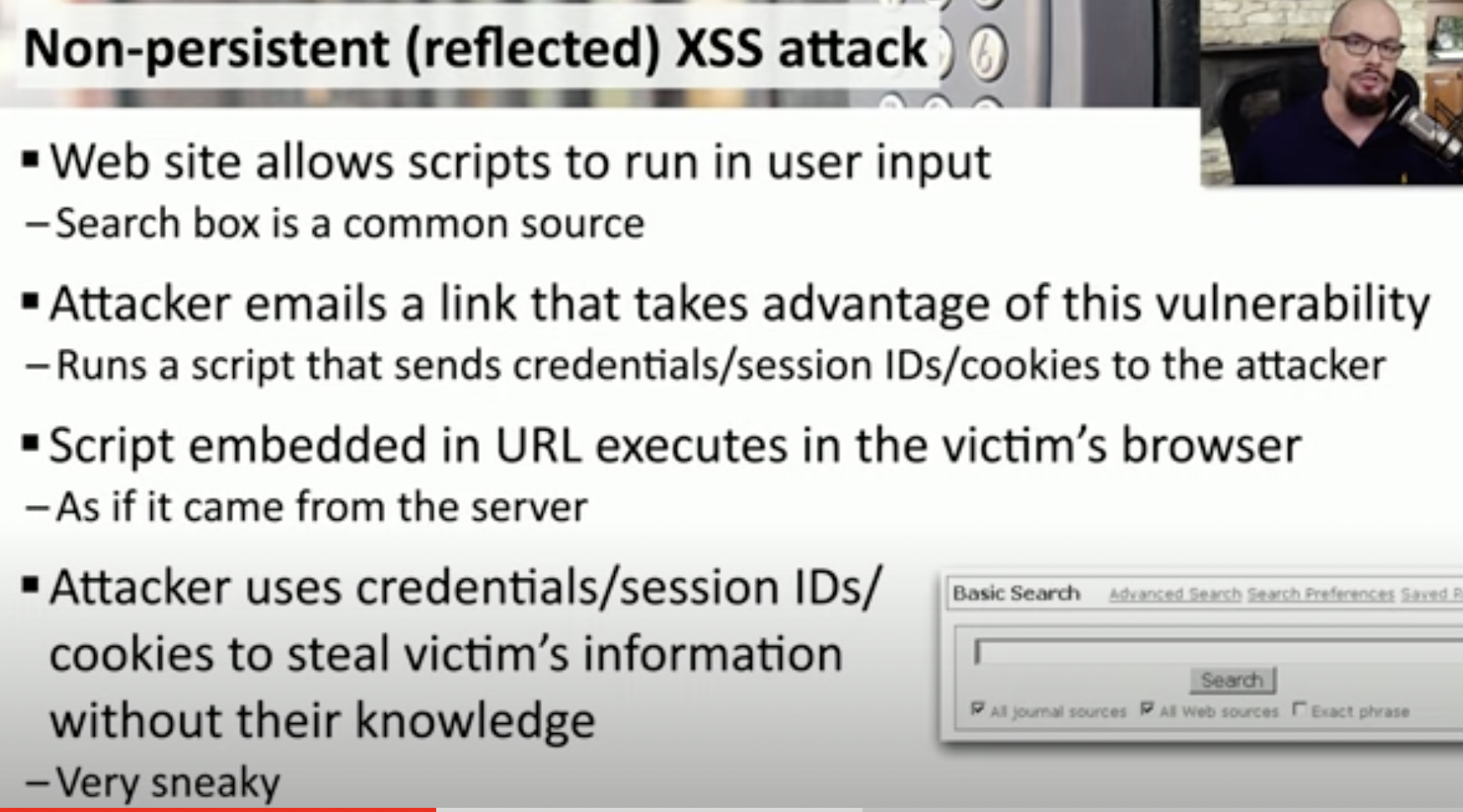
Non persistent (reflected) XSS process
Usually takes advantage of the search box or any user input
![Schermata 2021-08-28 alle 12.05.18.png]()
Persistent (stored) XSS
Everyone who accesses a malicious page runs a script
Subaru Hacked
![Schermata 2021-08-28 alle 12.10.10.png]()
Protect against XSS
![Schermata 2021-08-28 alle 12.11.54.png]()
Injection Attack
In what an injection attack consists of?
You basically add some informations into a data stream.
The most known protocols where we can inject data?
HTML, SQL, LDAP, XML …
SQL Injection
You modify an SQL request and gain access to the database
The shorter SQL Injection?
or ‘1’ = ‘1
XML Injection
You can modify XML Requests, and if they’re not validated you could do some serious damage
XML stands for Extensible Markup Language: a set of rules for data transfer and storage
LDAP stands for
Lightweight Directory Access Protocol
LDAP Injection
You modify the request to manipulate the results
DLL stand for
Dynamic Link Library
- The 4 steps of a DLL Injection
- A Malicious ‘process B’ attaches himself into ‘Process A’
- Process B allocates some memory into Process A for the DLL library
- Copies the DLL into Process A
- Process A runs the DLL as part of himself
Why the last step is genius?
Because Process A could have more right and permissions than a malicious process B
Buffer Overflow
In what this attack consists?
Overwriting a buffer of memory.
Spilling over into other memory areas
What is a really useful Buffer Overflow?
One that the attacker can control and that doesn’t cause issues to the system
![Schermata 2021-08-28 alle 12.29.10.png]()
Replay Attacks
Replay Attack
You use the data of someone else and replay them to be him in the network
Hackers will take thin informations through Network tap, ARP Poisoning, a malware in your pc…
If the hacker gains access to the Network he could take some serious useful informations…
Pass the Hash principle
The attacker redirects Hash of username and password to himself and gains access to the server
How to prevent this types of attacks
Using encrypted tunneling like SSL or TLS
Salt the encryption
How can a cookie f**k you?
If the cookie stores the session ID someone who has access to that cookie could login in your session.
![Schermata 2021-08-28 alle 12.41.00.png]()
Ways an attacker could perform some sort of Replay Attack and useful tools
![Schermata 2021-08-28 alle 12.44.30.png]()
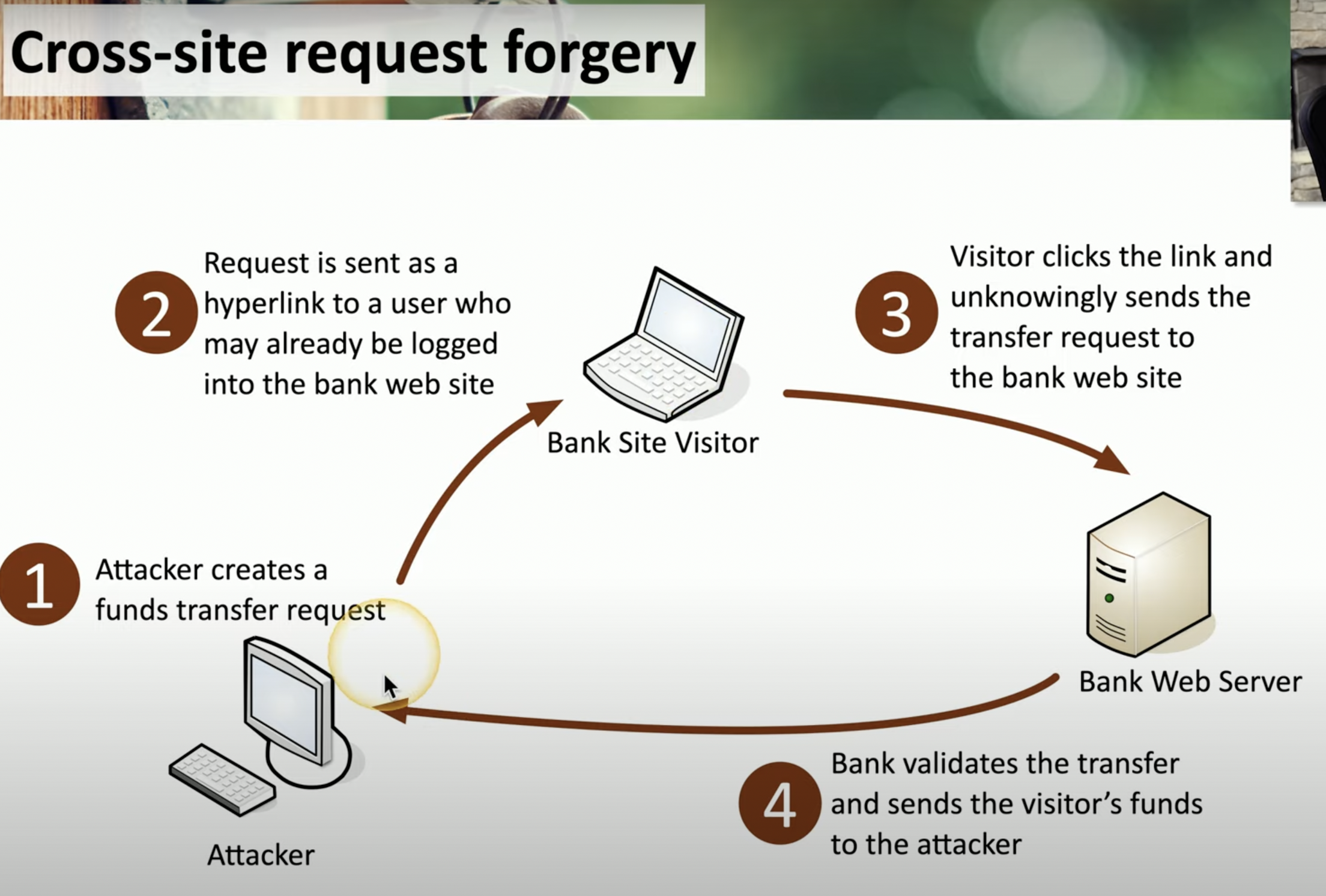
Request Forgeries
Cross site request explain
![Schermata 2021-08-28 alle 14.56.19.png]()
Cross site request forgery Acronym
XSRF
It’s also called one-click attack, it takes advantages of the trust that a web application has for the user
![Schermata 2021-08-29 alle 15.56.32.png]()
How to Prevent a one-click attack?
The application should have some sort of anti-forgery technique
Usually it’s used a cryptographic token to prevent forgery
What is a SSRF
Server site request forgery
The attacker will find a vulnerability in a web server and than send some sort of script
![Schermata 2021-08-29 alle 15.59.23.png]()
Capital One Attack
![Schermata 2021-08-29 alle 16.02.02.png]()
Driver Manipulation
Why is a driver a potential security issue if manipulated?
Because it has a very powerful interaction with the operative system, and because it often is trusted by the OS
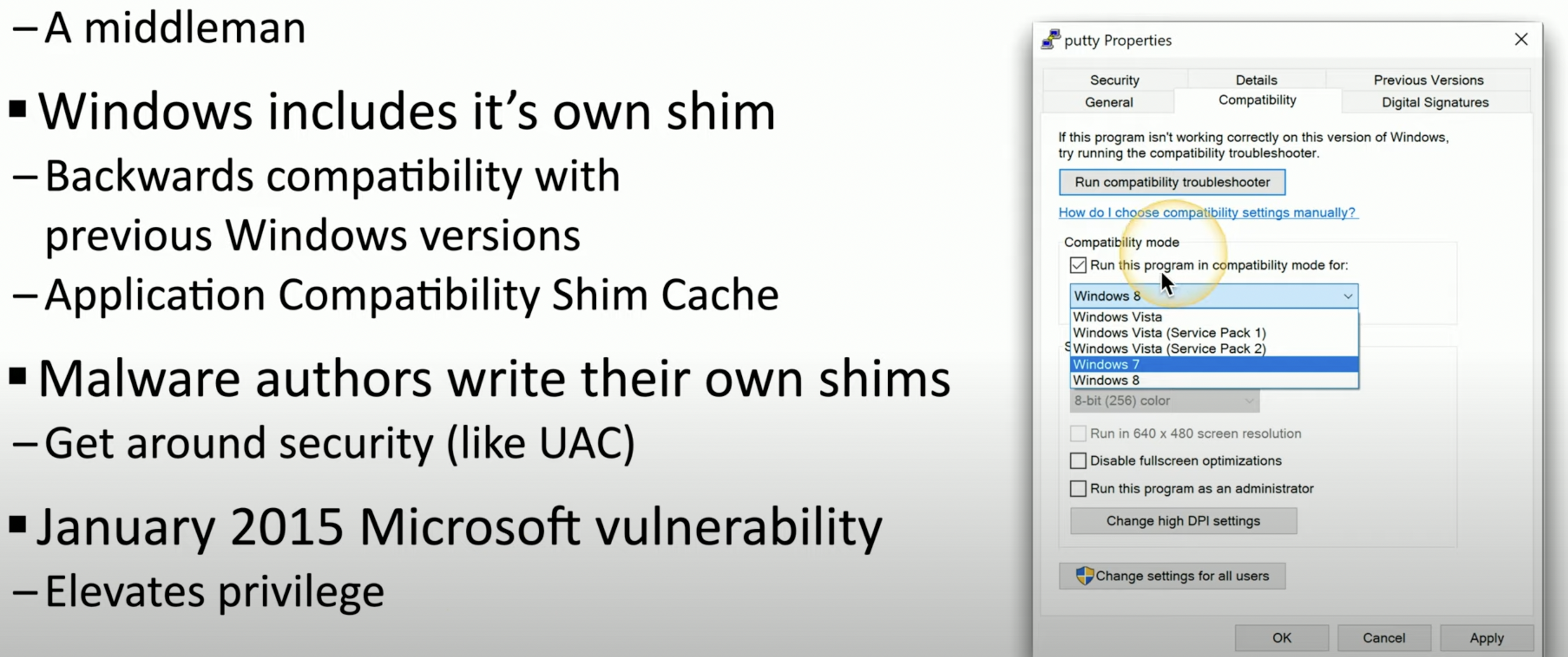
What is a Shimmer?
Something that stays in the middle. usually something that fills gaps
In IT, what is a Shimmer?
![Schermata 2021-08-29 alle 16.10.40.png]()
In what ‘Malware refactoring’ consists?
It consists in a metamorphic version of some existing malware. This version could not match the AntiVirus Standard and could not be blocked
What could an hacker refactor?
![Schermata 2021-08-29 alle 16.14.56.png]()
SSL Stripping
In what an HTTP downgrade consists?
It consist in an attack where the hacker wants to see what’s in a Stream Flow. It uses ARP spoofing or a rogue access point, or somewhere like that.
You can see it’s a SSL stripping or HTTP downgrade because the page that normally would have been encrypted it’s not. (the term stripping means that the SSL protocol is stripped away)
![Schermata 2021-08-29 alle 16.23.58.png]()
Acronym SSL (… socket …)
Secure Socket Layers
Race Conditions
Consists in
Taking advantage of simultaneous events to alterate normal flow of a website
![Schermata 2021-08-29 alle 16.28.29.png]()
Other Application Attacks
Memory Vulnerabilities, 1 upside 1 downside
If you can write to the memory you have almost complete control over a system but at the same time is really difficult to find a memory vulnerability.
NULL Pointer Dereference
If an hacker can send the pointer to a NULL section it can cause a Denial of Service
Overflow Attacks
If you put something in the memory and causes an overflow you can actually manipulate memory in your advantage: you write into sections of memory that were intended not to be written in.
What is a Directory traversal
There are some vulnerabilities that can cause an attacker to move outside of the scope and access files in a server.
API Attack
Application program …
API stand for
Application Program Interface
An attacker would try to find vulnerabilities in the communication Path between the API communication path, that is very similar to the http GET one, except that the majority of the time API protocols are used in mobile applications
Resource Exhaustion
Any attack that causes a Denial of Service through the resource exhaustion.
An example is a zip bomb: compressed 4.2kB of data, if you try to open it becomes 4.5 PetaBytes that’ll exhaust your pc
DHCP Starvation
![Schermata 2021-08-30 alle 15.24.36.png]()
1.4
Wireless Common Attacks
- BlueJacking
- BlueSnarfing
- Rogue AP
- Evil Twin
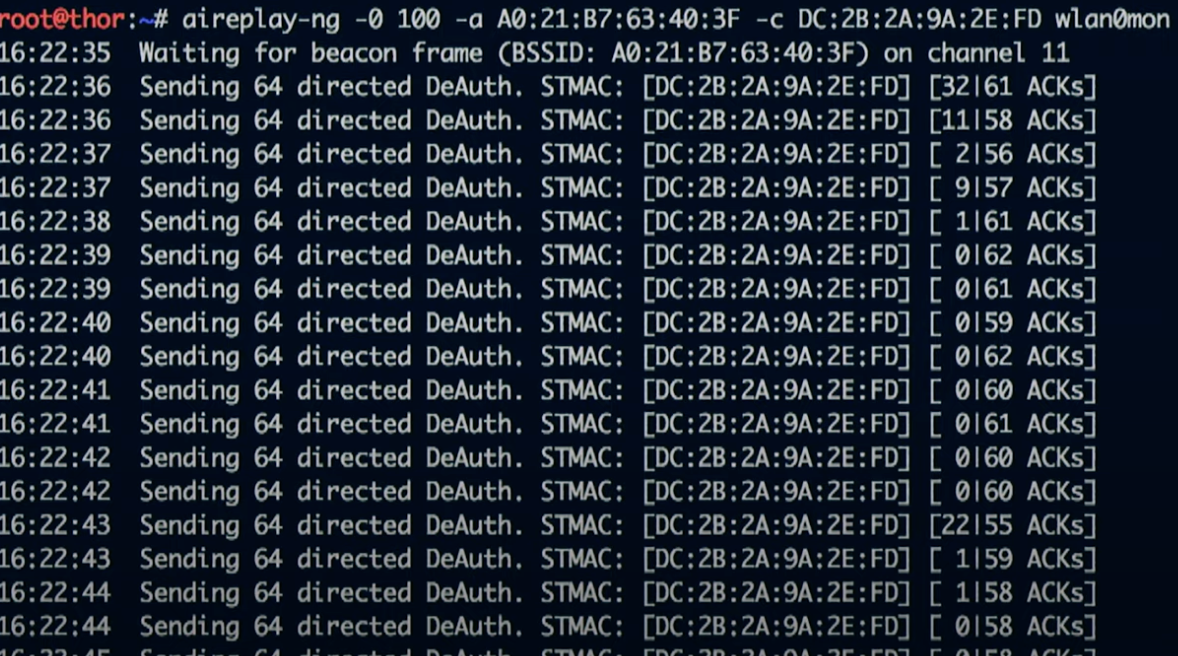
Wireless Disassociation Attack
Wireless deauthentication
a Wireless DoS attack. The attacker forces you to disconnect from the Network
How does this attack works?
You send ACKS to denial of service. aireplay-ng
![Untitled]()
Wireless Jamming Attack
RF Jamming
Stands for Radio Frequency Jamming
The goal is to decrease the Signal to noise Ratio. It could happen even by turning on a Microwave
Wireless Jamming Attack
The attacker could send costant random bits in the same frequency of the Access Point (AP) and cause a DoS
RFID and NFC Attacks
RFID
Radio Frequency Identification
![Schermata 2021-08-30 alle 16.10.23.png]()
NFC (near…)
Near Field Communication
![Schermata 2021-08-30 alle 16.16.48.png]()
NFC Security concerns
![Schermata 2021-08-30 alle 16.17.57.png]()
Randomization of Cryptography
nonce
a pseudo-randomized number (for the nonce - per l’occasione
Initialization Vector (IV)
Salt used in WEP
Salt
Added to the password and then encrypted to differentiate hashes even for accounts with the same passwords
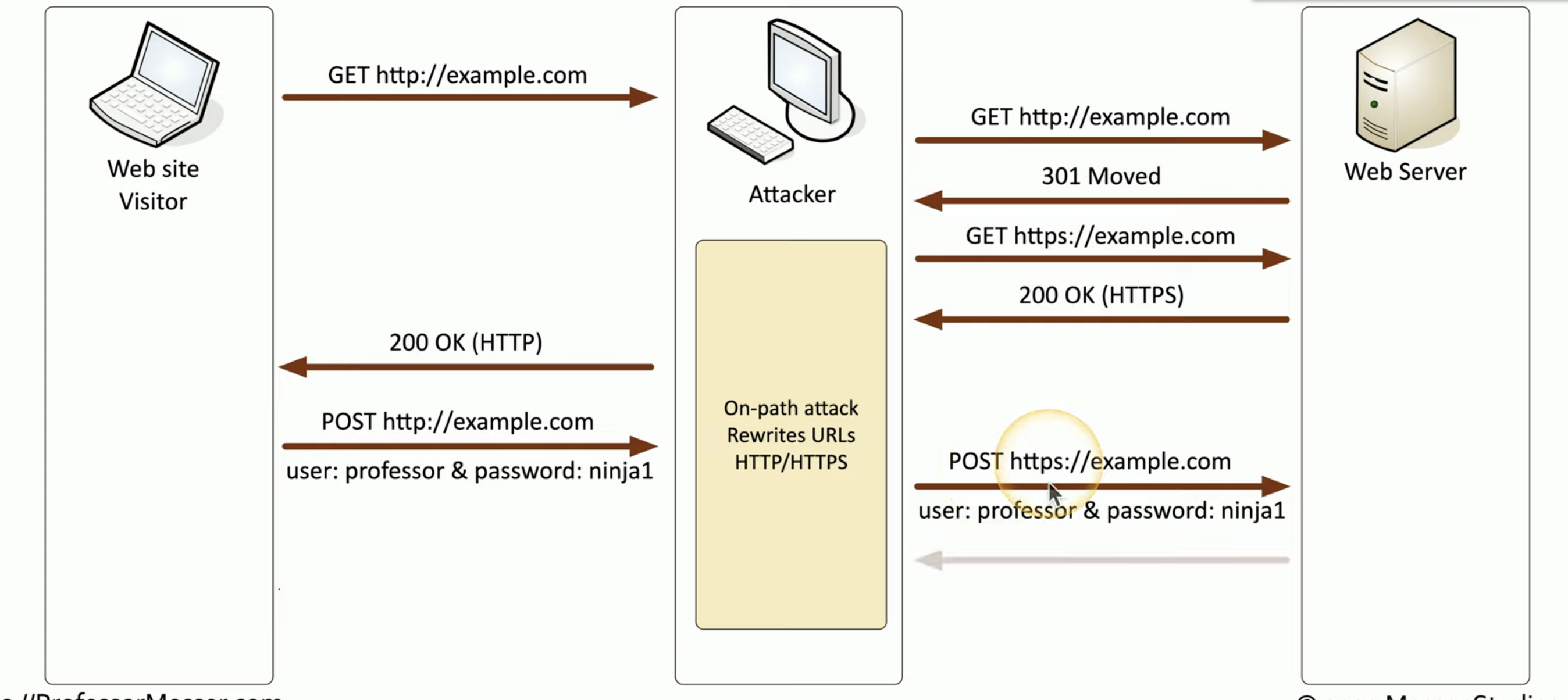
On-Path Attack
What is Spoofing
![Schermata 2021-08-30 alle 16.44.36.png]()
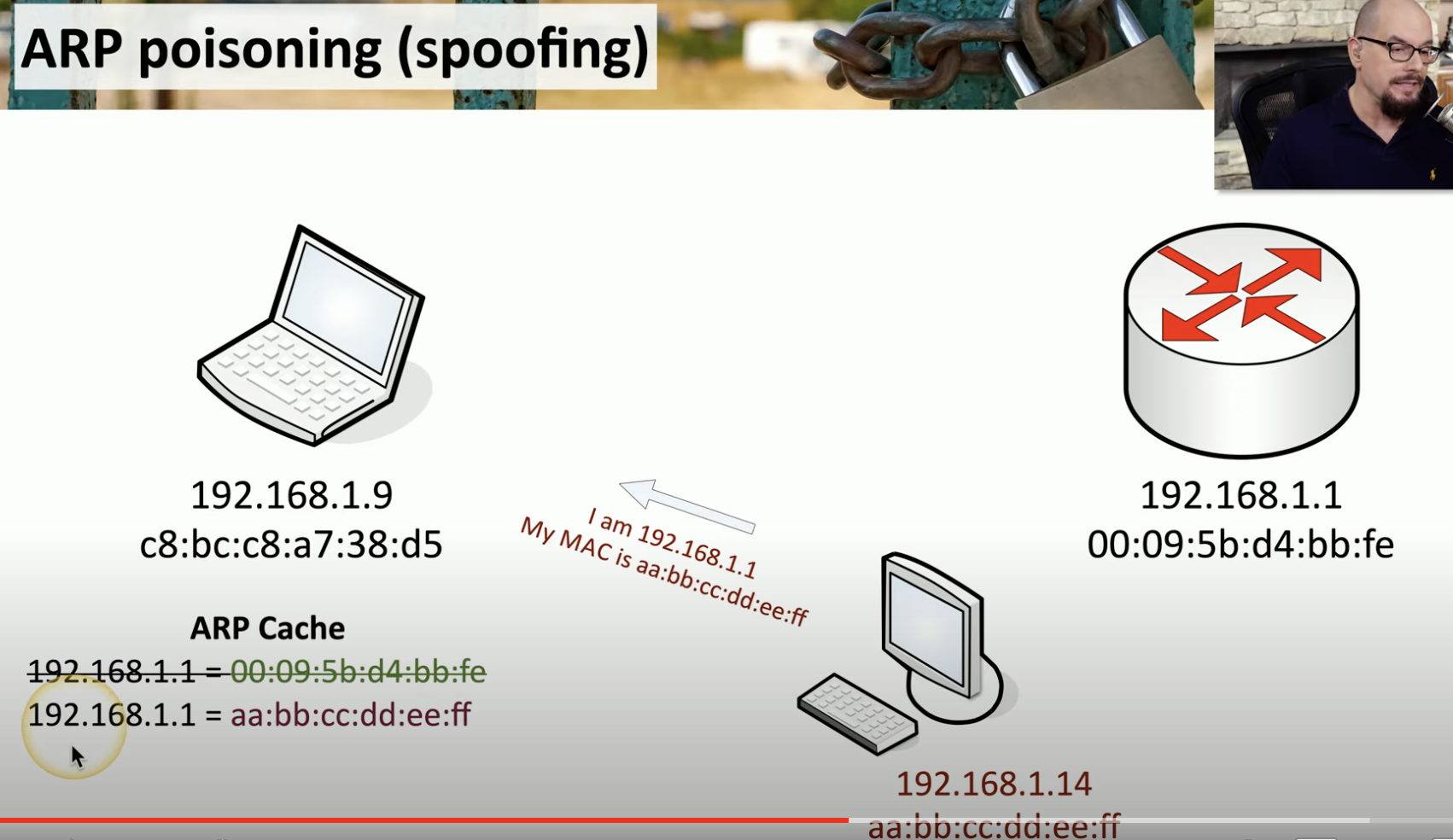
What’s APR and how it’s done
ARP Poisoning Routing
On-Path Browser Attack
Malware. It provides an on-path attack and let the attacker see all the data unencrypted.
If you just login into your bank the malware registers the credentials and sends them
MAC flooding and Cloning
MAC flooding
The attacker sends lots of MAC addresses to the switch, that fills up the MAC table and doesn’t know where to send datas anymore, so it forwards all the traffic in broadcast like an hub
MAC Cloning
Modify Source MAC address to match someone else’s
![Schermata 2021-08-30 alle 17.12.49.png]()
DNS Poisoning
DNS Spoofing / poisoning
If an attacker gets access to a DNS Server he could change the IP where a particular URL is related. That IP contains something malicious
What is most common than DNS Spoofing
Domain Hijacking
That an attacker gets access to the domain registration, so he can change everything without having actual physical access to the server
URL Hijacking
![Schermata 2021-08-30 alle 17.21.05.png]()
Domain Reputation
![Schermata 2021-08-30 alle 17.23.41.png]()
Denial of Service
DDoS
Distributed Denial of Service Attacks performed by BotNets
DDoS amplification
![Untitled]()
Malicious Scripts
- Automated Attacks
- The script is as fast as the computer
- No typing or delays
- No human error
- Automate the attack
- The hacker is on borrowed time
1.5
- Difference between threat actors and Attack Vectors and Attack Surface
Attack Vectors Examples
- if the attacker has physical access
- Keyloggers
- Reset of the administrator password
- Connect USB and copy data
- Cause DoS by breaking something
- Wireless Vectors
- It’s better to change default password from the router
- You can’t allow Rogue Access Points
- Especially Evil Twins
- Email Vectors
- Phishing attacks
- Deliver the malware to the user
- Attach it to the message
- Social engineering attacks
- Invoice scam
- Supply Chain Vectors
- Be secure by third parties
Cloud Based vectors
Publicly-facing applications and services Mistakes are made all the time Security misconfigurations Data permissions and public data stores Brute force attacks -Or phish the users of the cloud service Make the cloud build new application instances Denial of service Disable the cloud services for everyone
Threats Intelligence
Automated indicator sharing
Intelligence industry needs a standard way to share important threat data • Share information freely
- Structured Threat Information eXpression (STIX)
- Describes cyber threat information
- Includes motivations, abilities, capabilities, and response information
Trusted Automated eXchange of Indicator Information (TAXII)
Securely shares STIX data
Indicators of Threats
Unusual amount of network activity Change to file hash values Irregular international traffic Changes to DNS data Uncommon login patterns Spikes of read requests to certain files
Threats Research
Governative Databases
National Vulnerability Database (https://nvd.nist.gov) CVE Data Feeds (https://cve.mitre.org)
RFC (request …)
Request for comments
RFC 3833 Threat Analysis of the Domain Name System -RFC 7624 Confidentiality in the Face of Pervasive Surveillance: A Threat Model and Problem Statement
1.6
Vulnerability Attacks
- What are 0-day attacks
Unsecured root accounts
![Schermata 2021-09-02 alle 14.54.35.png]()
Error messages
![Schermata 2021-09-02 alle 14.55.16.png]()
Weak encryption
![Schermata 2021-09-02 alle 14.57.12.png]()
Insecure Protocols
![Schermata 2021-09-02 alle 14.58.40.png]()
Default Settings
![Schermata 2021-09-02 alle 15.00.35.png]()
Open Ports and services
![Untitled]()
Not up to date softwares
![Untitled]()
Third Party Risks
Supply Chain Risk
![Schermata 2021-09-02 alle 15.17.32.png]()
Vulnerability Impacts
- Identity Theft
- Billions of dollars
- Financial Loss
- Reputation Impact
- Availability Loss
1.7
Threat Hunting
Threat hunt
![Untitled]()
Intelligence fusion
![Untitled]()
Data Fusion
![Untitled]()
Automation of cybersecurity process
![Untitled]()
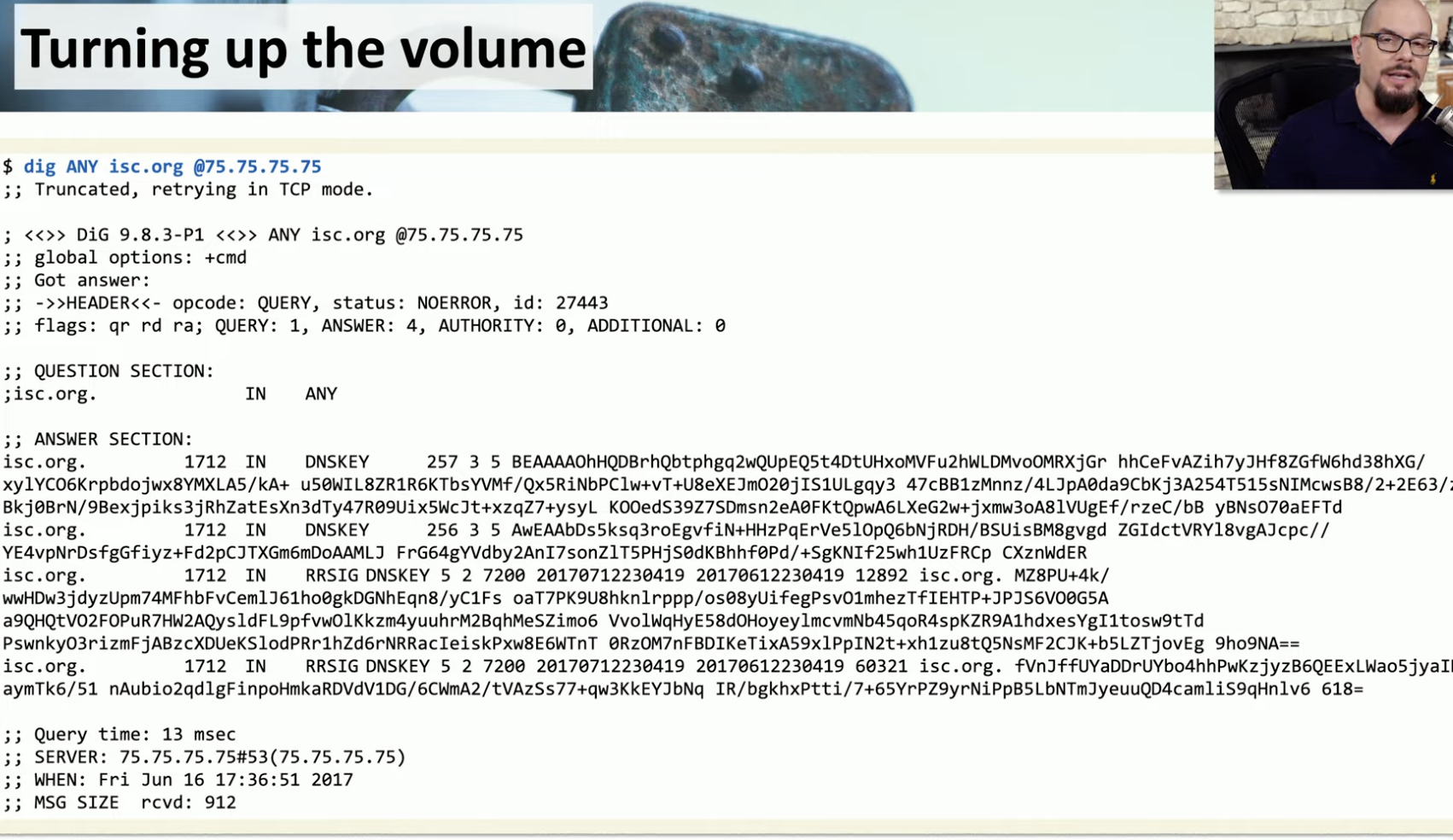
Vulnerability Scans
Scans
We have to collect as much datas as possibile to find any possible vulnerability.
example: look at the terminal and tell me a possible vuln of 192.168.1.1
![Untitled]()
What Scan Types you know?
We could use powerful scanners to identify vulns or we could:
![Untitled]()
Scan log review
![Schermata 2021-09-08 alle 13.48.10.png]()
What do we mean by false positives and how we handle them
![Schermata 2021-09-08 alle 13.49.55.png]()
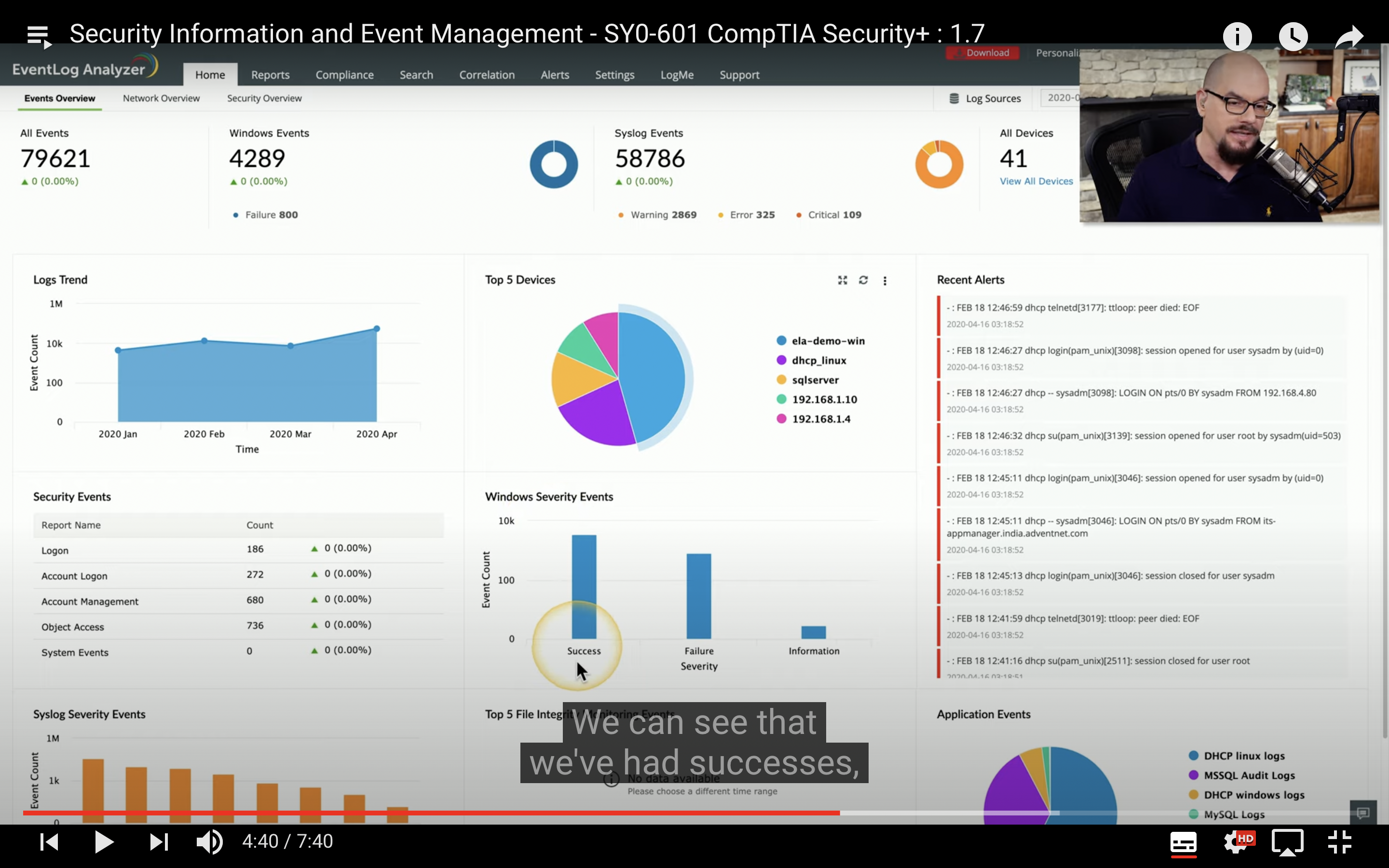
SIEM
What is a SIEM?
It stands for Security Information and Event Management
It’s a place where we store Logs aggregations and storage in long term
How do you make every device store logs in the same way?
Using the standard syslog format.
Usually it’s integrated into the SIEM
What to store in a SIEM
Data inputs Server authentication attempts VPN connections Firewall session logs Denied outbound traffic flows Network utilizations Packet captures Network packets Often associated with a critical alert Some organizations capture everything
![Schermata 2021-09-08 alle 13.59.33.png]()
2.0 - Architecture and Design
2.1 - Explain the importance of security concepts in an enterprise environment
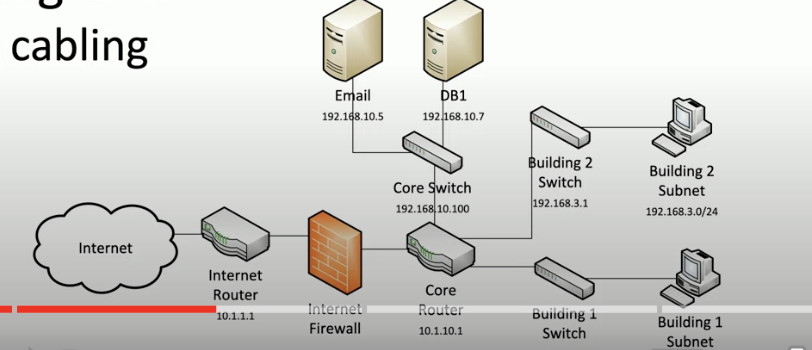
What’s a network diagram?
a documentation of wires and devices
![Untitled]()
What’s baseline configuration and what do we mean by integrity measurement checks?
documentation of the environment to properly secure it
integrity measurement checks need to be updated often
How do you create standard naming conventions?
By standardizing names and making conventions easy to understand by anyone
example for a device
![Untitled]()
Why do we need an IP schema?
it’a standardization for network devices who need an IP.
we need it for organizational purposes
How does stored data is affected by data suvreignty?
data sovreignty indicates the laws and the regulations. Local Law could affect where data can be stored and how.
GDPR is the General Data Protection Regulation in the EU
What do we apply to data to protect PII?
Personal identification information could be protected by data masking or data obfuscation
Where could data at rest stored? How do we protect it?
SSDs, HDDs, flash drives etc… we protect it by providing encryption
How do we provide encryption to data in transit?
through transport encryption, maybe using protocols like TLS or IPSec
Why attackers could prefer attacking data in use?
data in processing is probably in plain text
What do we mean by tokenization
we use tokens to replace sensitive data with a non-sensitive placeholder
What’s IRM? What’s is purpose?
Information Rights management. We need it to control how data is used and to restrict access o unauthorized users. The purpose is to limit the attacker.
How could we define DLP?
Series of rules and systems to prevent data loss
- Geographical considerations
What’s the most important thing we do to limit the impact of an attack?
A response and recovery control plan, where we define how to identify and contain an attack
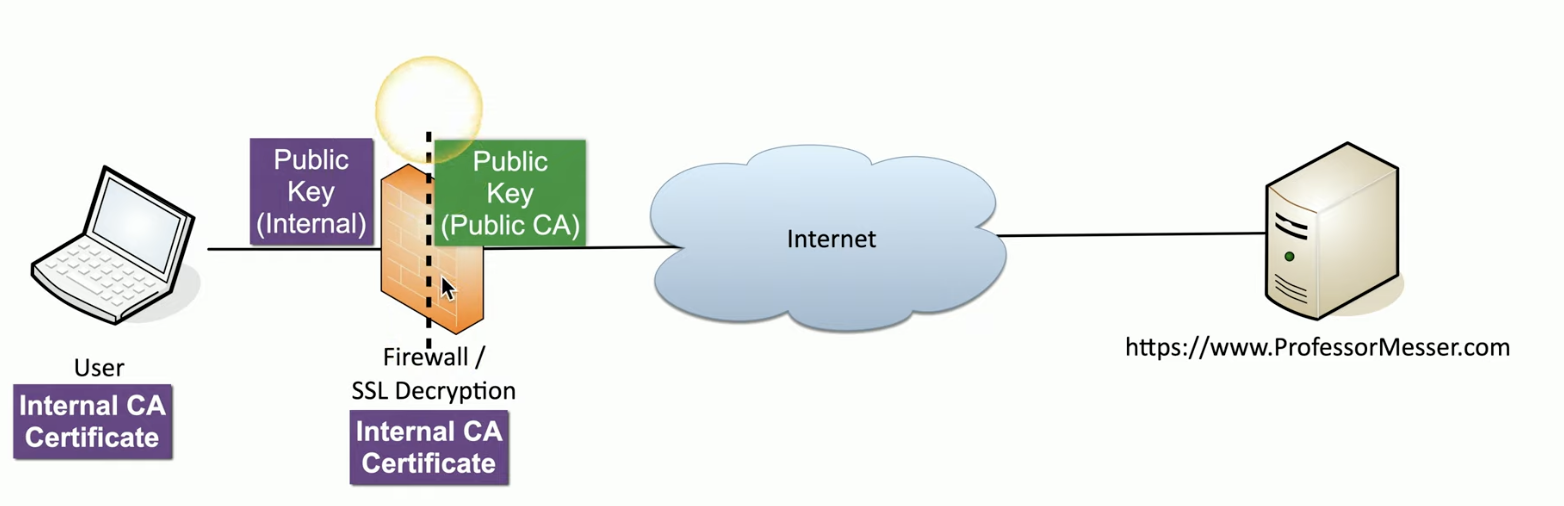
What’s SSL and TLS inspection based on?
It’s based on trust. like the trusted CA list in our browser.
Why might we need TLS proxy?
To add a security layer. Also anything that’s going inside can be decrypted, analyzed and then send to the hosts in the network.
![Untitled]()
What does APIs do? We need to do some considerations about security?
Application program interface is used to communicate and control applications. We have to ensure that security is provided not only for the user but also for the application, in a way that attacker could not interfere with API messages
What’s WAF?
Web Application Firewall, filters API commuinication
Why is site resiliency necessary?
Becouse as an incident could occour at any time, having backups and sites where sensitive data is stored to provide redundancy is crucial.
What’s the difference between hot-site, cold-site and warm-site?
Hot-site: a place where you keeps an exact replica of your data that is constantly updated
Cold-site: empty building that you own
warm-site: Is usually a location that has racks ready and waiting
Difference between honeypots and honeyfiles
an honeypot is a part of the network set up as virtual trap to bait attackers and block them from accessing the real network. honeyfile is just a file ex: passwords.txt
What do we mean by fake telemetry
With machine learning computers are able to identify malicious code in a big chunk of data. fake telemetry is a tecnique used by attackers to trick the AI by using their own machine learning software and ensure that their code will not be identified by the software
What’s a DNS sinkhole?
A malicious attack where the DNS request from a host is responded with invalid or incorrect IP address to redirect us to an external server or to a malicious server.
2.2 - Cloud / Infrastructure as a code
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QNoQCZdWEOE&list=PLG49S3nxzAnkL2ulFS3132mOVKuzzBxA8&index=68
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GIgp6BGr4C8&list=PLG49S3nxzAnkL2ulFS3132mOVKuzzBxA8&index=69
2.3 - Summarize secure application development, deployment, and automation concepts
Why is sandboxing useful in secure deployments
Sandboxing provides an isolated testing environment with no connection to the production system etc
In the environment of secure development there are some stages that involves Testing, Staging, Production and QA. What does the last of this listed stages consists on?
Quality Assurance consists on verifying that anything works as intended
Staging?
It’s the final test of the data, and the last chance to test the application before it goes to production
Why for any application is good to have a security baseline?
To ensure security is provided as soon the application is deployed, and to review every instance in detail when software updates are made
Why is orchestration the key to cloud computing?
‘Cause provisioning and deprovisioning is made almost istantaneous thanks to automation. Orchestration is also moving things around to your needs.
When talking about Secure coding techniques, what does server-side vs client-side execution\validation stand for?
![Untitled]()
How could memory management be a security concern?
If you’re not mindful of how memory is used, without input validation the data could overflow to the crash of the app or worse. Always make sure your data matches the buffer sizes
Why SDKs could be a security concern?
Software development kits could contain programming lenguage that does almost all the work but still it’s application code written by someone else so it might not be as secure.
How does an application could risk Data exposure?
By not encrypting data when stored or by displaying informations on the screen
How we call it when an application binary is different for one machine to another, but has the same functionalities.
Software diversity
- How can we have a set of automated responses
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=f4ciE3zjKe4&list=PLG49S3nxzAnkL2ulFS3132mOVKuzzBxA8&index=75
2.4 - Summarize authentication and authorization design concepts
Auth-methods
biometrics
MFA
2.5 - Given a scenario, implement cybersecurity resilience
How do we call when you provide redundancy between multiple geographical areas
Geographic dispersal
What’s multi-path I/O and how it differs from RAID
continue
2.6 - Explain the security implications of embedded and specialized systems
Generally, what are embedded systems?
Very specific devices with a purpose that perform a function, like trffic lighters or wearables
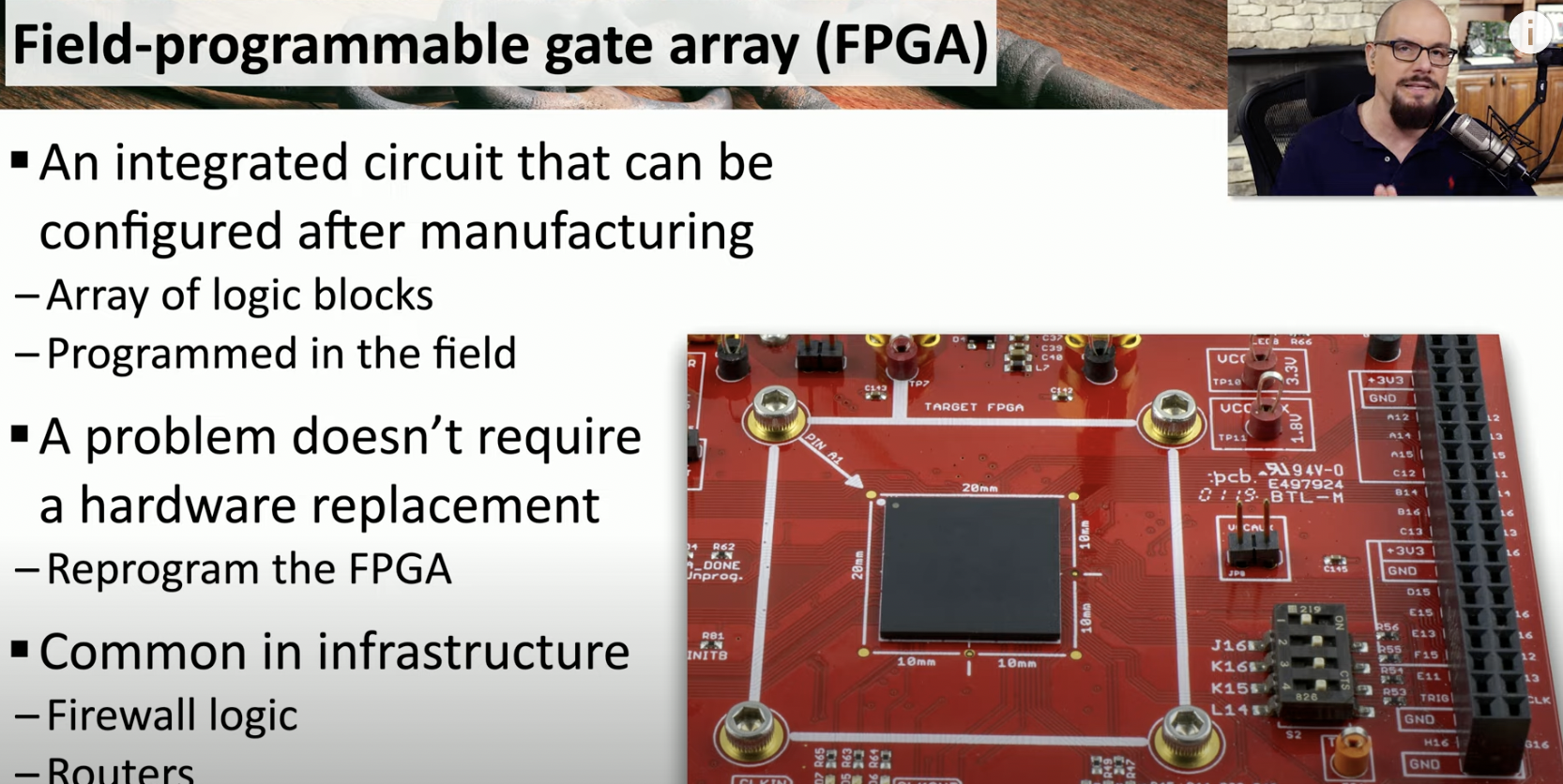
If you think of a SoC embedded system, what three programmable devices come in your mind?
RPi
FPGA Field programmable gate array
![Untitled]()
Arduino
How would you use a SCADA?
I would use a Supervisory control and Data Acquisition System (like a multi-site Indutrial control System) to monitor my company embedded systems (like power generators, manifacturing equipment, logistics, …) and have distributed control that grants real time informations and system control.
You wouldn’t want to connect this to any external networks.
What’s the number $1^1$ concern about IoT devices?
They’re embedded systems connected to your network, and may not be secured well (weak default credentials, store personal data…)
What type of specialized embedded systems would you find in medical syst, vehicles, aircrafts and sensors watching our utility use? just imagine and find problems with each of those, especially if compromised
Difference between VoIP and POTS
Voice over IP uses internet communication systems whereas Plain old Telephone service used analog phone lines
HVAC stands for?
Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning. They provide availability expecially in large and fragile data centers
What type of license would you need to fly a Drone?
a federal license
How sophisticated is usually an MFD?
A multifunction device is usually very sophisticated and use complex firmwares, as they integrates multiple services in a device (ex: scanner and printer in a MF Printer)
What’s the main feature of a RTOS?
Real time operating system uses processes based on deterministic procedures, they also are sensitive to security issues and always need to be available.
What’s the connection speed over 5G?
up to 10gigabits per second, with real performance between 100-900 Mbit/s
How the 5G impacts the IoT world?
For the bandwidth and the more processing functionalities thanks to the speed
What’s a Subscriber identity module card? what’s is purpose? what’s International Mobile Subscriber Identity?
SIM, to connect the IoT device to wireless network providers. An unique number to identify the user (Authentication)
Difference between Narrow-band and baseband radio. Where do we find those?
Narrowband means longer distance and slower speed, where basebands use a single frequency to communicate (narrow use a more large variety of frequencies)
We find narrowbands where there is SCADA equipment or sensors where there is an oil field
Name the Zigbee standard and what ISM bands it uses
IEEE 802.15.4 PersonalAreaNetwork(PAN) to make the IoT devices communicate and It uses frequencies 900MHz and 2.4GHz in the US
- Constrains like power source, compute power, network connectability, cryptographic obfuscation, inability to patch, no authentication of use, contained functionalities (often single function), low cost, no direct access to system or software.
3.0 - Implementation
3.1 - Given a scenario, implement secure protocols
3.2 - Given a scenario, implement host or applications security solutions
What does EDR has changed when attackers learned how to fool signature-based AV solutions?
Endpoint Detection and Rejection started to monitor behaviors of the machine, thanks to process monitoring, Machine learning and behavioral analysis
Why is DLP sometimes a very challenging solution to implement?
Data loss prevention often requires multiple solution to implement, becouse the sources and the destination of the data we want to protect are so many.
NGFW main features?
Next Generation firewall are network layer security implementation, often called as Application Layer Gateway, Stateful multilayer inspection or Deep Packet Inspection.
A NGFW has multiple features for security, such as malware and attacks detection of the upcoming packets through decryption, inspection and re-encryption
Is Host Based FW hardware or software? where does it run?
Host Based Firewall is a software solution that runs in every endpoint device. If you’re in a corporate network, you would manage them in a centralized way
What’s HIDS?
Host Based Intrusion Detection System.
How HIPS differs from HIDS?
HIDS uses log files to detect attacks, whereas Host Based Intrusion Prevention System stops the attack before it starts. It often is built in the application
What are the 3 different part of booting a system, regarding to security chain of trust? How could the boot sector be infected?
Secure boot, trusted boot and measured boot. Through rootkits (kernel level malwares)
How is Hardware Root of Trust is achieved?
Through Hardware Security Module and Trusted Security Module. In particular the TPM helps with cryptogragraphic processes.
How does the TPM protects the unique keys burnt into the chip?
There is some kind of dictionary attack protection
The Software Root of trust is achieved through?
Through UEFI BIOS secure boot. Secure boot means checking the integrity of the bootloader thanks to a digital certificate
How does the Unified Extensible Firmware Interface trusts updates to the Firmware?
BIO includes the manufacturer’s public key Digital signature is checked during a BIOS update BIOS prevents unauthorized writes to the flash
What comes after a UEFI Secure Boot ?
A phase called Trusted Boot.
Here the OS kernel is checked for manomissions and then the Kernel itself will verify other startup components.
What’s ELAM?
Early Launch Anti Malware
It will check every driver’s integrity and won’t load automatically the drivers who failed the test
What happens during Measured Boot?
Only happens if there’s a centralized control over multiple hosts
Hashes of drivers and firmware are stored into the TPM of each single endpoint, then encrypted and send to the Attestation Center for identification of any unexpected change.
What’s called the process of sending hashes from the TPM to the Attestation center?
Boot Attestation
How would you manage sensitive and temporary informations such as Credit Card numbers?
Through tokenization, in a way that the data isn’t even stored in the database
Salting and Hashing?
What function serves the QA team during the development of an application?
The quality assurance team tests if the application is secure
What’s the process of normalization?
Some sort of input validation, with cecks and corrections.
Why is fuzzing a type of dynamic analysis?
Fuzzing is sending test inputs, often random
Name a security concern with cookies?
If they contain sensitive informations and someone gets access to them. Cookies are not designed to store personal informations.
How does HTTP header prevent XSS attacks?
Headers are like an allow list, as they communicate with the browser sending instructions.
What authority involves Code Signing?
Certificate Authority to sign the code and provide integrity
What’s SAST and what’s an issue correlated to their processes?
Static Application Security Testing is automated code analysis and an issue could be false positives
Why would you backup registry?
Registry is a database of rules and settings. If you change critical informations you would want to roll back;
Difference between SED and FDE.
Self encrypting drive uses opal standard to encrypt informations. FDE totally encrypts a chosen drive.
3.3 - Given a scenario, implement secure network designs
When we say active / active we’re referring to __.
Servers
Round robin is a particular algorithm used to meet _______ necessities of the load balancer.
scheduling
Session persistence to review
What type of segmentation is being used if there’s an air gap?
Physical segmentation.
Other types of segmentation are logical (VLANs) and virtual.
The incoming connections to your network apps are being redirected from the firewall to a network designed to be separated from your actual internal network. What is this area of your network called?
It’s a demilitarized zone (DMZ) or screened subnet.
What’s the difference between extranet and intranet?
An extranet is some sort of DMZ that requires additional authentication, whereas the intranet is a particular area of our network that is accessible only from the inside (you being on the VLAN or connected to it through a VPN)
Explain the concept of East-West traffic and South-North traffic.
In a network environment like a data center, EW traffic refers to the operations between local devices in the same data center(so it has fast responces), SN traffic instaed refers to inbound and outbound traffic, that usually has more security put in place as the outbount connections are mostly untrusted.
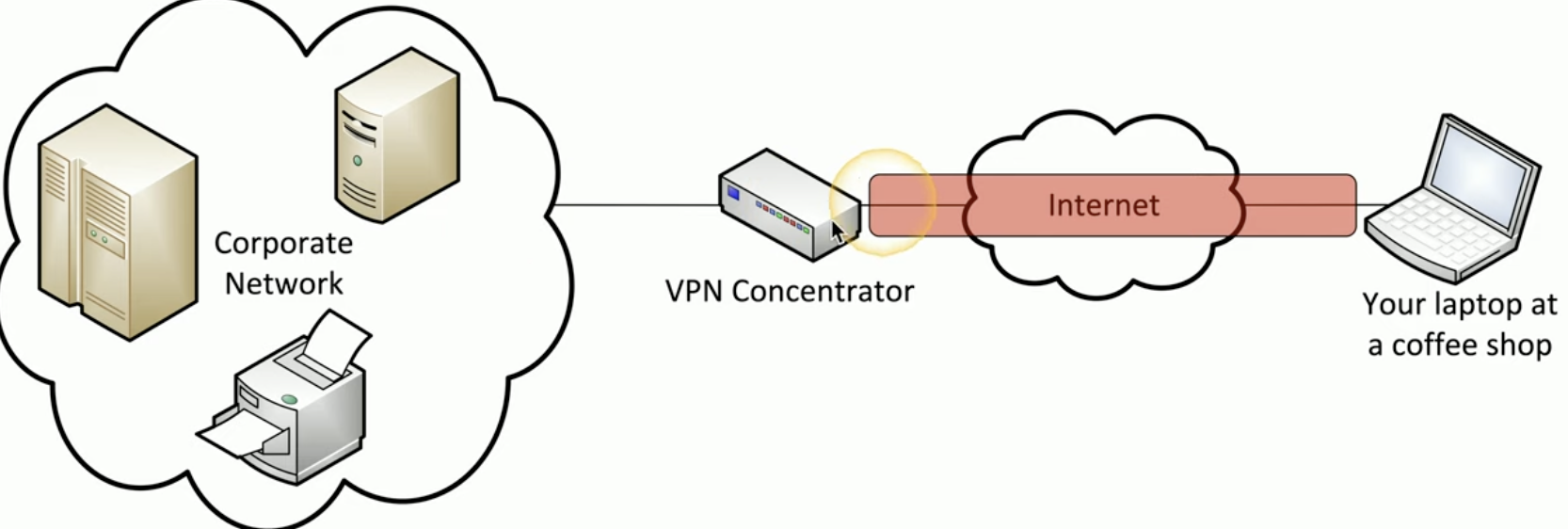
What’s a VPN concentrator?
![Untitled]()
What protocol grants tunneling functions?
L2TP Layer 2 tunneling protocol
What two protocols comprehend IPSec?
AH: authenticated header. Used only during tunnel mode
ESP: encapsulated security payload used turing tunneling mode and transport mode
During transport mode the header is sent over the clear
Difference in the data path of Split vs Full tunnel in VPN.
During Split Tunnel the data is sent over the tunnel only when communicating with the internal network connected to the VPN, while using normal communication for connecting with other servers.
In Full tunnel The VPN concentrator is necessary, becouse it sends the data to the destination, whatever it might be.
Do some sort of broadcast storm control exists? Where can we find it?
Yes, on switches
How do loop prevention was implemented in 1990
With the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP)
Explain BPDU guard and why we use it.
To prevent loops the STP uses learning states and quite few time to determine if there are more switches being attached. If you set a port to be able only to listen traffic from devices that are not switches, you are limiting the STP work and using what Cisco calls ‘PortFast’.
The Bridge Protocol Data Unit guard shuts off the interface if a switch is attached to it.
Where could you encounter DHCP snooping? What’s its purpose?
DHCP snooping is the concept of monitoring a switch for preventing and real-time searching for unauthorized DHCP servers to be connected to the network. so DHCP snooping is some sort of protocol analyzer (most of the time default software in the switch) on a layer 2 device.
Why would we use Media Access Control Filtering?
You would use MAC filtering to control that only authorized MAC addresses can be connected to the network, the problem with this is that there is no security in level 2 that prevents MAC addresses to be spoofed and impersonated, so MAC filtering is more of an administrative tool than a security guard.
What’s a sinkhole address?
DNS can prevent end users to address known dangerous sites. A sinkhole address is the address we’re redirected to.
Out of band management REVIEW What’s QoS?
Quality of Service, it refers to the quality we need to perform. We call the process of prioritizing some services over others “Prioritization”
Port taps are a security concern. How do they work?
Port taps sit in the middle of links and capture a copy of network traffic. They could be physical or sofware based.
A Port mirroring software in a Cisco switch would be called __
SPAN or Switched Port ANalyzer
What would be the benefits of using a Monitoring service for your network?
Organizations that provide Monitoring Service 24/7 for networks usually provide a staff of cybersecurity experts at a Security Operations Center (SoC).
They do constant monitoring and patching, they can respond to threats faster and they can also ensure your legal compliances like HIPAA, PCI DSS.
If you have some files that sould never change, how would you identify when changes occur?
through monitors of the file integrity (FIMonitoring tecnique)
like SFC (System File Checker) for Windows or Tripwire of Linux.
What’s WAF? Why is it needed when complying with PCI DSS?
Web application Firewall. It filters the web traffic for your web based applications.
PCI DSS is the payment card industry data security standard, and it applies to your website if you accept card payments. In this standars of rules there’s also the need of a WAF.
Name the main difference between traditional firelwalls and NGFW in traffic filtering.
Traditional firewalls filter traffic through port number, NGFW through the application being used and through traffic monitoring
What’s the difference between stateless and stateful firewalls?
Stateless FW do not keep track of traffic flows, and only specific rules are applied to traffic. They are now almost deprecated.
Stateful FW keep track of traffic flow through the creation of a session table, whenever a communication is set, and this session table remembers certain rules that can not be changed after the communication is set. so it’s much secure
Expecially for our source port of the communication, stored by the firewall the server would not be able to communicate with us if the destination port does not match
example: tcp/15442 → tcp/80 (us → server) … tcp/80 → tcp/15543 blocked !!!(server → us)
What security an UTM provides?
an Unified Threat management solution can provide all-in-one security appliances
It serves as a web security gateway that constantly looks for malwares, does spam filtering, URL filtering, Content inspection and whatever the manifacturer wants.
Why is a NGFW more intelligent than an UTM?
UTM are physical devices provided by vendors, they can not contain anything we need. A NGFW is based on the Application layer, being a software the capabilities are more.
What’s ACLs referring to Firewalls?
Access control lists that allow or disallow traffic based on tuples, rules gouped in categories.
What’s a posture assessment?
When device is connected to our corporate network we may want to perform healt-checks, like:
- Is it a trusted device? Is it running anti-virus? Which one? Is it updated? Are the corporate applications installed? Is it a mobile device? Is the disk encrypted? The type of device doesn’t matter Windows, Mac, Linux, iOS, Android
What’s the difference between NAC with agent and agentless NAC?
agented Network Access Controls run software on devices attached to the network to perform healt-check. in particular:
- Persistent agents are permanently installed onto a system
- Dissolvable agents run during the posture assessment and terminates when they’re no longer needed
agentless NAC are performed to systems that present operating system default NAC checks. Those often run during logon and logoff but to have specific and added functionalities you may want to implement an agent.
What are the main edge control you have to implement?
Firewall rules
Why is NAT a proxy? What type of proxy is it?
NAT is the network address translation, that operates at a network level and just like any other proxy, it collects the internal traffic of a network and after some operations, in this case the IP translation it forwards it to the outside internet. And viceversa.
It’s a network level proxies. Most proxies are application based.
What’s a forward proxy? also called internal proxy. And a reverse proxy?
Mbare un proxy interno al tuo network che controlla che non visiti siti p0 rno
A reverse proxy does the same but checks the requests of the web server instaes.
Why wouldn’t you send data to an Open Proxy?
It’s a third party, uncontrolled proxy. It might be malicious as they function like forward and reverse proxy at the same time, and they could modify the requests and the responses.
NIDS and NIPS, what are and their main difference.
Network intrusion detection system and prevention system are methods we use to secure our networks.
They watch the traffic and detect intrusions (alarm or alert) or prevent them to get into the network (real time stop)
inline and out-of-band monitoring(passive)? how do you stop intrusion in both cases?
If the IPS is inline with the other devices it’s able to stop the traffic being send.
If you’re using out-of-band-monitoring the IPS is external to the traffic and just analyzes a copy of the packets, but if it recognizes an intrusion it could sent a TCP reset to the hosts and reset the communication (blocking it). If the attacker uses UDP this won’t work
Identification Technology are diverse. Name 4 of them for an IPS.
- Signature based: exact same packet
- Anomaly based: something out of regular schemes
- Behavior based: it recognizes the possible behavior of attackers
- Heuristic: based on AI
How do we set a Jump Server
We secure a protected device and SSH/RDP/VPN to it. This is dangerous if you don’t secure that device well.
Why would you store your private keys in a HSM if you’re in a large data center?
Couse they are made to do it
Why would you use Sensors and collectors?
To aggregate informations from all your network devices and have them in one place.
SIEM, IPS and syslog servers are collectors.
3.4 - Given a scenario, implement and configure wireless security settings
What message should we send over a wireless network to provide integrity?
a MIC: message integrity check
Explain CCMP over WPA2
WPA2 uses CCMP (counter mode / CBC-MAC) → cyber block chaining, message authentication code protocol
CCMP provides confidentiality through AES and integrity (Message integrity check) with CBC-MAC
Explain GCMP over WPA3
only difference from WPA2 is the use of Galois / counter mode protocol, that provides GMAC (Galois Message authentication protocol) for the MIC
What’s the PSK problem with WPA2?
Someone could capture the pre-shared key and try to brute force that hash to retrieve the actual Password.
How does WPA3 solves the PSK problem?
They’ve added additional security features, no more 4handshakes and hashes. Mutual authentication and perfect forward secrecy (the session key is thrown away when done)
What does Simultaneous Authentication of Equals serves and when is it used?
Simultaneous Authentication of equals is used with WPA3 as a solution to the PSK problem and derives from the Diffie Hellman process to share session key. Sometimes this is referred to as the IEEE dragonfly handshake
What wireless authentication method would you implement in your house? and in a corporate network?
House: PSK or shared password
Corporate: Additional security with the 802.1x standard (Radius, Tacacs or Ldaps maybe)
What would you use a captive portal for?
To authenticate to a network and be able to use the internet
WPS enabled or disabled?
Disabled. It uses 8 digit pin.
Why EAP is called EAP?
The Extensible Authentication protocol serves to the wireless solutions in order to auhenticate users, and it’s extensible as often is used in conjunction with 802.1x or LDAPS, TACACS, RADIUS…
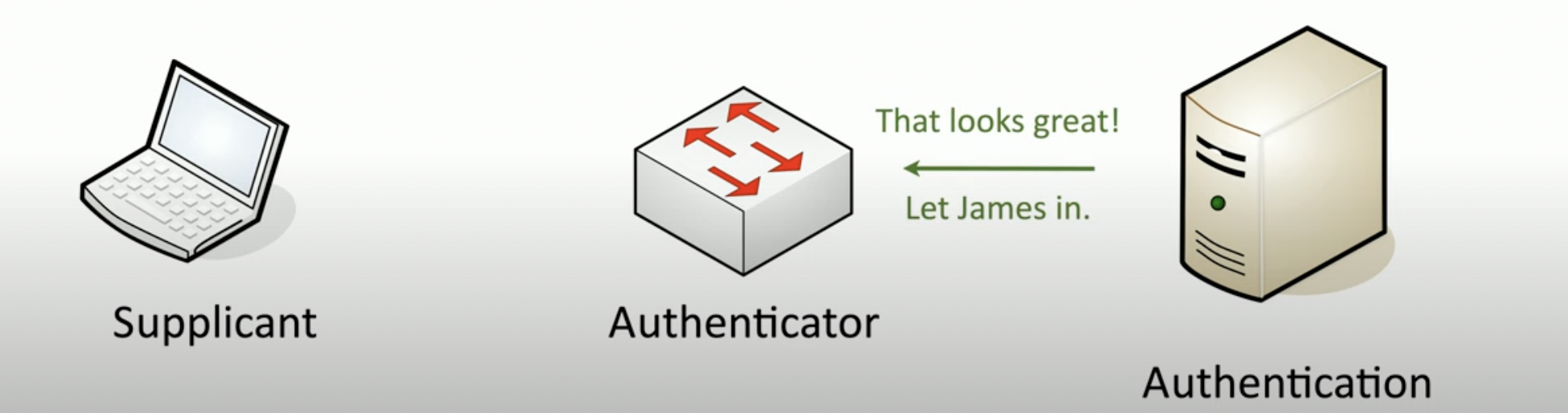
Tell the process of authentication through 802.1x and EAP
The supplicant asks the authenticator to gain access, the authenticator does not provide it but it sends back an EAP request, followed by a response by the supplicant with the username.
After, the authenticator provides the username to the server and enstablishes a secure connection to ask for the credentials, that if provided correctly are send in the backend (server) that ultimately authenticates the user
![Untitled]()
EAP-FAST stands for? what’s the shared secret name?
Extensible Authentication protocol - Flexible Authentication via Secure Tunneling. It sets a secure TLS tunnel to share a protected access credential (PAC)
This is often used with RADIUS
PEAP is created by Cisco, Microsoft and RSA. What it uses instead of PAC?
Protected EAP. It uses a digital certificate and it’s often used with MSCHAPv2 databases.
Users can also authenticate through Generic Token Card
EAP-TLS has something different from every other EAP. What’s that?
The authentication is mutual so the digital certificate are stored in both the supplicant and the server
EAP-TTLS
Tunneled EAP with TLS. Is used to use other authentication method through this tunnel
RADIUS Federation uses what protocol to authenticate?
Mostly EAP. Remote authentication dial in User service
What’s a site survey?
When implementing nad installing wireless solutions you need to plan layouts and identify wireless signal strenght (through heat maps)
What would you do if you had to analyze wifi?
I would use any packet analyzer that listens to all the informations send through the wireless.
How do you avoid interferences when installing multiple wifi access points?
Using different areas of the spectrum (using overlapping channels).
Placing them in places not near interferences
How do you manage wireless access point centrally?
Through a Wireless controllers.
3.5 - Given a scenario, implement secure mobile solutions
What are cells referring to cellular networks?
The coverage of the antennas, that operates in certain frequencies
What’s the security concerns someone could face by just connecting to a cellular tower?
someone could track your location or monitor the traffic being send to the tower
Name three local security problems with wifi
data capture (if you do not encrypt your data), on path attacks (middleman or rogue access attacks) and DoS attacks by interfering with the frequencies
What’s PAN referring to Bluethoot?
Personal area Network - high speed comunication over short distances
what’s RFID and what are its most common uses?
Radio frequencies identification is a small chip using radar tecnology (it’s powered using radio energy and this provides bidirectional communication). It’s used for everything that needs tracking.
What’s NFC and why is it related to RFID?
Near Field Communication it’s a two way wireless communication based on the closeness of the two devices. It’s commonly used for payments and it uses RFID technology.
How does GPS determine the position?
Using 4 satellites near you and comparing the timing difference between them. Sometimes also wifi and antennas help the process
What’s MDM? and BYOD?
Mobile device management - Bring your own device
What’s the best way to manage mobile applications centrally?
Using an allow list so that only approved application can be installed
What’s MCM and what’s the best way to manage it?
Mobile content management is the way of handling data in mobile devices. We’ll use DLP capabilities to prevent sensitive data loss, and we could also ensure all the data in the device is encrypted
Why would we want to implement remote wipe?
To delete everything even if you don’t know where the device is
What’s it called when you want to limit certain functionalities when device is in a certain area?
Geofencing
What’s a security concern with push notification?
That everyone can see them just by looking at your screen
What’s context-aware authentication and how it differs from 2FA?
It’s a type of authentication that builds a profile of the user who’s tryin to authenticate, like IP address, geolocation etc…
How do you separate personal data and corporate data when a BYOD policy is adopted?
By creating different partitions on the device with different types of data. This is called containerization.
This allows to manage the two portion of device in a separated way (storage segmentation)
FDE stands for? Where would the key stored in a corporate mobile device network?
Full disk / device encryption. The key is often stored by the MDM.
What’s the equivalent of an HSM in mobile devices?
Micro SD Hardware Security module, used for security services and secure storage
What’s the purpose of an UEM ?
an Unified Endpoint management solution is an evolution of MDM that incorporates mobile and non-mobile devices to provide the same security policies in an unified solution
What’s the best solution to manage applications in an enterprise?
Through a Mobile application management solution (MAM), that provides lots of features like remote data wipe and monitors application use
SEAndroid is an NSA project that makes sure security is provided in android devices. How the method of data access is changed since SEAndroid is used?
Android devices used to use DAC, now by default having MAC we found that every application is sandboxed and isolated. now access to sensitive low level datas are centralized to the manifacturer and the user has no access to them
In your corporation you want to make sure your corporates do not install applications out of the scope of the business. What would you implement?
Mobile Device Management
What’s a carrier locked phone?
When a phone’s firmware is locked to use only the provider who supplied the phone (Vodafone or Verizon for instance)
What’s OTA?
Over the air, it often refers to firmware updates.
How do you make sure the phone camera of your corporates is off in a certain area of the corporation?
Through MDM.
What’s OTG?
On the go USB connection features on mobile devices
When should you disable geotagging with your MDM?
When you don’t want location metadata to your corporates’ files.
What’s the mobile wireless standard?
IEEE 802.11
How do you make two IoT devices communicate directly?
Thanks to wifi ad hoc or WiFi Direct.
Why shouldn’t you allow Tethering in your corporate network?
To prevent someone get malicious access to the network through the insecure thetering of a mobile device, instead of keep the use of the corporate secure network.
What are we referring to if we say COPE? What’s a similar policy where you get to decide the device?
Corporate-owned personally enabled device. The organization keeps full control of the device.
CYOD Choose your own device.
What policy should you implement if you don’t want your corporate devices to be personally used?
You provide corporate owned devices.
What’s a VDI / VMI?
A virtual desktop infrastructure / virtual mobile infrastructure keeps data separated from the device. The VMI is generally a server and the device access data and application stored on it remotely.
4.0 - Operations and Incident Response
4.1 - Given a scenario, use the appropriate tool to assess organizational security
Command to determine the route of a packet
tracert:Windowstraceroute:Linuxtakes advantage of TTL in the ICMP protocol
Command to gather informations from the DNS servers
nslookup(deprecated)digCommand to know your IP address and configurations
ipconfig: Windowsipconfig \allifconfig: LinuxCommand to test reachability
pathping: Windows (both ping and tracerouteping:Linux and WindowsCommand to get Network statistics
netstatnetstat -a -b -n-a: active -b: show binaries (Windows) -n: do not resolve names
Command to view the local ARP table
arp -aCommand to view the device’s routing table
route print: Windowsnetstat -r: Linux and Unix
Command to retrieve data using URL
curlCommand to find and scan network devices
nmapCommand to craft a layer 3 packet / scan a network
hping/hping --scan p0-pCommand to gather OSINT on company or domain
theHarvesterCommand to run many recon tool in a single framework
sn1per
Command to run a scan from a proxy to not be identified
scanless-tURL-sserviceCommand to enumerate DNS informations
dnsenumFramework to scan vulnerabilities
Nessus
Framework to run an executable in a safe environment
Cuckoo
Command to concatenate a file to the standard output
cat: Linuxtype: WindowsCommand to view the top part of a file and command to view the last lines of a file
headtail-nnumber of linesCommand to find text in a file
grepCommand to change permissions for a file in Linux
chmodCommand to record informations and save them in the syslog file
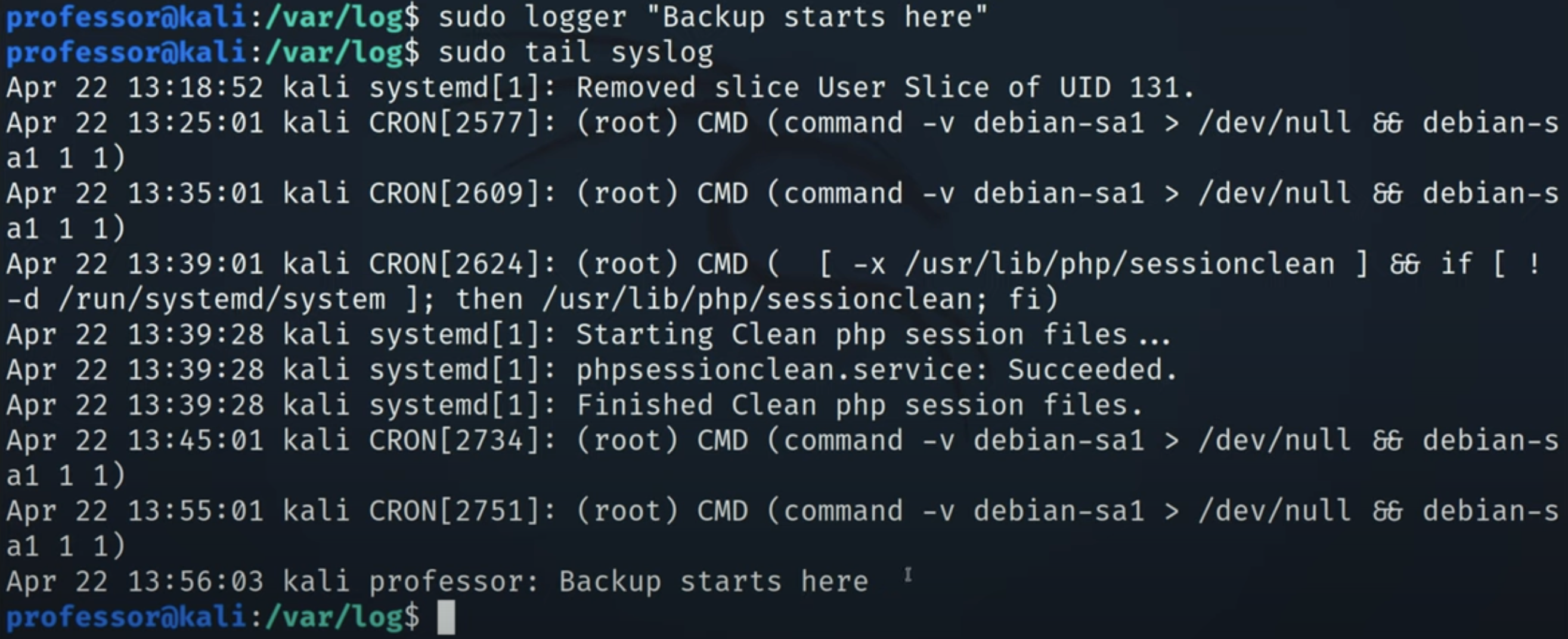
logger![Untitled]()
A file with a
.ps1is native of what OS?Windows - script for Powershell
What is the purpose of OpenSSL
A toolkit for SSL/TLS libraries
You can build X.509 certificates and use OpenSSL for encryption and decryption and other
What’s the most utilized Packet Capture and replay framework?
WireShark
Command to capture packets and display traffic on display
tcpdumpCommand to replay and edit packets, used to test security devices
tcpreplayyou can edit packets and send them over the network, and hopefully your intrusion prevention system will block it
You have to create a disk image for forensic analysis. What linux command will help?
ddif=/input/pathof=/output/pathCommand to copy in memory contents
memdumpYou want to edit the Hexadecimal contents of a file/disk/RAM in Windows. Name the framework you would use.
WinHex.exe
What’s the FTK imager purpose?
Is a framework for forensic drive imaging used in Windows
What’s Autopsy purpose in forensics?
It’s a tool to view and recover data from storage devices, capable of extracting many different data types
Name two exploitation framework
Metasploit Framework
SET Social Engeneering Toolkit
What would you use if you had to brute force a password?
a Password Cracker
What’s called the process of completely remove data from a drive?
Data sanitization
4.2 - Summarize the importance of policies, processes, and procedures for incident response
What’s an IRP?
Incident Response Plan
What’s in the NIST SP800-61?
A computer security incident handling guide by the National Institute of Standards and Technology.
It comprehends the lifecycle of an incident response:
- Preparation
- Identification (Detection and Analysis)
- Containment
- Eradication and Recovery
- Post-Incident activities
Main processes of Preparation in IRP
Having policies and backups
Main processes of Identification in IRP
Detection and Analysis
Main processes of Containment in IRP
Isolation of threats in sandboxing environment
Main processes of Eradication and Recovery in IRP
Recovery from an incident, get things back to normal and recover of the system. Often you’ll need to patch the issues that permitted the exploit
What we mean by Exercises in IRP?
Exercises stand for tests to our system, tests that need to be done before an incident ever occurs
What’s a Tabletop exercise?
We get everyone in a meeting and talk through a simulated disaster
What’s an exercise that will test processes and procedures, involves all groups and helps identify missing steps and missing steps?
A Walkthrough
What’s called a test of a specific event?
Simulation
Who are Stakeholders? What do we mean by Stakeholders management?
Customers
We want to keep a good relationship with our Stakeholders.
Why is communication plan important?
Having good plans for organization of the communication between the people involved in processes and procedures is crucial.
You may want to have communication plans for Corporates like the CIO, CISO and other Internal non-IT personnel, like human resources or legal departments, or maybe external contacts like system-owners.
What’s DRP and what does it covers?
a Disaster recovery plan is a comprehensive plan with the informations needed to respond to a disaster. It is part of the Business Continuity plan
it covers the plan to provide continuity of the business if general disasters occur (natural disasters, system failures, human-created disasters, …)
What’s a Continuity of operations planning (COOP)?
A planning of how normal operation would change if disaster occurs
What does Retention policies cover?
Retention policies are policy on how to retrieve data when needed
What’s the diamond model of intrusion analysis
a scientific principle based structure to help analysts understand intrusions
Where would you search a specific attack vector?
In the MITRE ATT&CK framework
When we refer to the seven phases of a cyber attack, what’s this chain of phases called?
Cyber Kill Chain
![Untitled]()
4.3 - Given an incident, utilize appropriate data sources to support an investigation
You have been notified of a trend change from the SIEM. What has happened?
There has been a change of normal patterns during the SIEM monitoring.
Explain the concepts of Sensitivity and Correlation you see in a SIEM dashboard.
The sensitivity is the setting of what information are warnings, what are urgent and what informations are just informational.
Correlation is something you set to combine and compare data from multiple sources and verify everything’s normal
Where do you find application log files in Linux and Windows?
Linux: /var/log
Windows: Event Viewer → Application Log
You have a web server that stores lot of log files. How would you manage them?
Send them to a SIEM
What would you use dump log files for?
Dump file from an application serves mostly to address some problem that occurred with that specific application
In VoIP what protocol logs the initiation of the call and other useful informations?
SIP / Session Initiation protocol traffic logs informations such as call setup, inbound and outbound
- In a Linux environment, what are the most popular syslog daemon?
- Rsyslog “Rocket-fast System for log processing”
- syslog-ng - syslog with filtering and storage options
- NXLogs - collects logs from many different types of log
In a Linux environment, some system logs are stored in a binary format for storage optimization. What is the tool that let us view this logs as plain text?
journalctlWhy do we need bandwidth monitors?
If the bandwidth is overly utilized, other resources may not work properly
What does SNMP, NetFlow, sFlow and IPFIX have in common?
They all have the capability of monitoring the bandwidth statistics
Where do we find metadata?
In lots of stored files like photos, emails and office files there are metadata with informations normally hidden.
What do we find in a NetFlow collector?
All the NetFlow data that this standard is capable to gather, normally all traffic flows and shared communication between devices.
What are the differences between NetFlow and IPFIX?
IPFIX is based on NetFlow v9, so they are not very different, other than the fact that IPFIX is newer
What data collector can gather accurate statistics from a portion of the actual network traffic, and can operate at level 2-7OSI?
sFlow
Name a protocol analyzer.
WireShark
4.4 - Given an incident, apply mitigation techniques or controls to secure an environment
How does an anti-virus application blocks a known malicious executable?
It would have hashes of the known malicious application and by finding something that matches it, the antivirus would block and quarantine it.
What’s the difference between Isolation and Containment concepts.
Isolation refers to infected devices
Containment refers to the sandboxing application policy of an OS
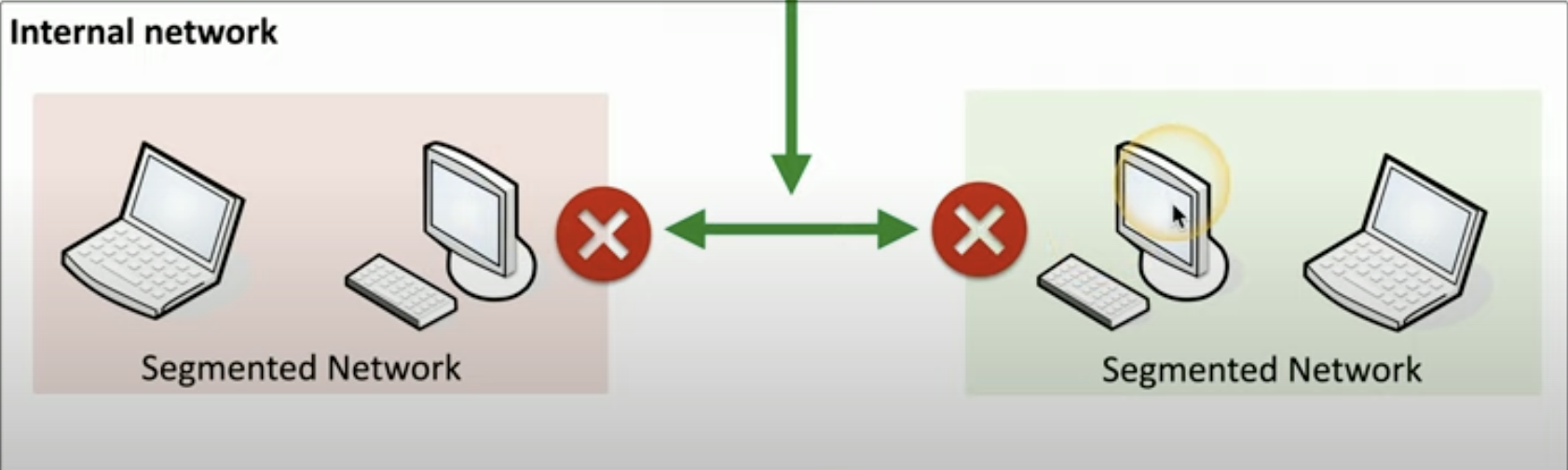
How do you prevent and mitigate an attacker from performing lateral movement in internal Networks?
Through segmentation of the internal network
![Untitled]()
What’s a SOAR? How is it linked to Runbooks and Playbooks?
Softwares for security that provides Orchestration, automation and response in order to make security teams more effective and efficient.
Runbooks and playbooks are standard procedures on witch the SOAR is set.
4.5 - Explain the key aspect of digital forensics
What document set guidelines for evidence collection and archiving?
RFC 3227
What data would you find in a Legal Hold?
Electronically stored informations (ESI) of different source and type, in ongoing preservation (an obligation to preserve data)
The main concern about admissibility of data would be
The legal authorization about holding that data
What’s the purpose of Chain of custody?
To maintain integrity
What would be your main concern about timeline sequence of events if you have both FAT and NTFS files?
FAT stores time in local time, whereas NTFS time is stored in GMT, so you would need to perform some time translation
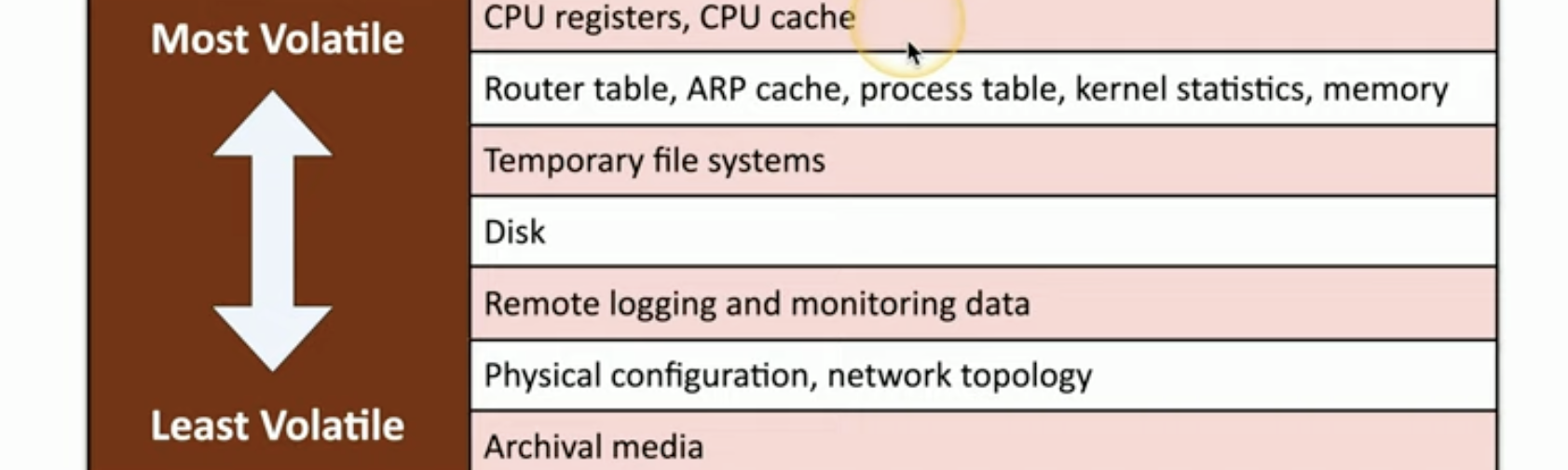
What are order of volatility?
![Untitled]()
The first step you would perform when dealing with disks in forensic analysis.
Drive image preparation (power down and remove of storage drive) and the imaging of the drive itself
Than forensic bit-for-bit cloning
You’re investigating a ransomware infection in a device owned by the corporation. What OS data would be useful to the forensic analysis of that incident?
Users, Processes, open ports and attached devices
You’re investigating a rootkit. what should your attention focus on?
Firmware modifications
What’s an Artifact in digital forensics?
Digital traces left by contacts.
Why Right-to-audit clauses should be part of a contract with a CSP when performing digital forensics?
Right to audit clauses it’s a legal agreement that is put in place to have the option to perform a security audit at anytime;
this gives the ability to verify the security even before a data breach occurs, and also defines how data should be shared and managed agreeing to terms and conditions.
What’s the main concern about jurisdiction / regulation of data when dealing with cloud computing?
The location of the data and the different jurisdiction and regulation of each zone the data is placed
When are ‘Data breach notification’ laws applied?
If some customers’ data were leaked Data breach notification law defines who gets notified and when
If we have a documentation of authenticity and a chain of custody, what type of attribute defines the function of both documentations?
Provenance
To obtain preservation of a mobile drive what should we do?
We should copy and image the drive
When we need to gather data needed by a legal process, what’ the process of obtaining that data called?
e-discovery
When we have non-repudiation we are sure ___ and ____ are provided to our data.
Integrity … authentication
Name two methods of providing non repudiation. (hint: 1 peer to peer; 2 public)
MAC : message authentication code where two entities can verify non-repudiation
Digital signature can ensure non-repudiation to anyone who has the public key of the signature.
In what the counterintelligence (CI) consists on?
In trying to stop someone trying to gather information on us through OSINT.
5.0 - Governance, Risk and Compliance
5.1 - Compare and contrast various types of controls
Name the three main categories of security controls.
Managerial, Operational and Technical
What’s the difference between control category and control type?
Categories are three and describe the way the control is implemented. The control type instead define the purpose of the control.
What category of control a phishing training program would be?
Operational, control implemented by people
What category of control are security policies?
Managerial, control addressing implementation and standard procedures
An anti-virus would be a __ control.
Technical, controls implemented using systems
Difference between preventive and detective control types.
Preventive is a control type that prevents the intrusion, detective a control type that detects it.
A preventive control can’t always detect an intrusion and a detective control can’t always prevent access to the system.
What’s a corrective control designed for?
To mitigate potential damage.
example: a backup site could mitigate an incident, an IPS can identify and block an attacker …
What’s a deterrent control designed for?
To discourage an intrusion
example: warning sign, fake CCTV
What’s the difference between Compensating controls and physical controls?
Compensating controls are just restores of something you do not longer have (do not stop an intrusion), whereas physical controls are real world security like fences or mantraps
5.2 Explain the importance of applicable regulations, standards, or frameworks that impact organizational security posture.
Who addresses the GDPR?
The general data protection and regulation addresses every company that holds PII
Who addresses the PCI DSS? How many control objectives does it contains?
The payment card industry data security standard addresses every company that holds and uses credit card for protecting them.
This act has 6 objectives
- Build and maintain a secure network and systems
- Protect cardholder data
- Maintain a vulnerability management program
- Implement strong access control measures
- Regularly monitor and test networks
- Maintain an information security policy
What’s the purpose of the CIS CSC?
The purpose of the Critical Security Controls by the Center for Internet Security are to explain implementation for cyber defenses.
It comprehends 20 key critical security controls, categorized in company sizes.
What’s the main framework utilized by federal agencies in the US?
The NIST (National institute of Standards and Technologies) $\darr$
RMF (Risk Management Framework)
It comprehends 6 main steps with processes to secure a set environment
Who does The CyberSecurity Framework (CSF) by NIST addresses?
CSF It’s a commercial framework for improving infrastructure security
you’re a commercial wanting to implement high level view of cybersecurity
![Untitled]()
Be able to tell the purpose of each ISO/IEC Standard: 27001, 27002, 27701, 31000.
ISO/IEC → International Organization for Standardization / International Electrotechnical Commission
The followings are standards by the ISO/IEC
- 27001 → ISMS (International security management system)
- 27002 → related to the previous, contains practice for information security controls
- 27701 → focus on privacy PIMS (Personal identification management system)
- 31000 → standard for international risk management practice
Be able to tell the difference between Type I and II in the Statement on Standard for Attestation Engagements number 18 (SSAE 18), and also the purpose of the SSAE 18.
This act comprehends a broad variety of audits that covers security controls.
- Type I audit → performed at a specific time
- Type II → performed for at least 6 month
The Cloud Security Alliance (CSA) published the CCM. What does this act covers?
The Cloud Control Matrix is a set of Cloud-specific security controls, divided in ‘standards’, ‘best practices’ and ‘regulations’ you need to follow in the coud.
What are secure configuration guidelines?
Guidelines that help you harden services you start that are not secure-by-design.
Services: Web servers, OS, Application servers, Networking devices
5.3 - Explain the importance of policies to organizational security
We have detailed documentation called AUP. Explain it’s functionality-
The Acceptable use policies covers lots of topics that address the company itself and restricts the use of IT according to legal liability
What does the Mandatory vacation policy tries to identify?
Frauds
Split Knowledge separates the details of some works in a way that is coherent with the ____ __ _______ policy.
Separation of duties
If you can’t ever leave your desk with some informations in your screen, how’s this policy called?
Clean desk policy
Who addresses an NDA?
A non disclosure agreement addresses a company and a third party entity
It’s purpose is to prevent use and dispersal of confidential information
How’s the set of standard procedures involved with hiring someone called? reversed?
Onboarding - Offbording
When talking about training programs, what’s CBT?
Computer based training, based on training at your own time with your own terms using your computer
SLA?
Service level agreement, minimum set of service terms (used between customers and service providers)
MOU?
Memorandum of understanding, informal letter with intents of parties. includes confidentiality informations. It’s not a contract but it lets both parties understand.
MSA?
Measurement system analysis,
If your company relies on measurements for the business, an MSA is used to test the quality of the measurement process and it serves also to address and calculate the uncertainty of the process
BPA?
Business partnership agreement, details of going into business together
EOL?
End of life for something. May continue to support the product
EOSL?
End of service life for something. Support is no longer available
NDA?
Non disclosure agreement - Accordo di riservatezza
Who’s the responsible of data privacy, accuracy and security?
The Data Steward
![Untitled]()
Difference between change management and change control
The change control is a formal process for managing change.